Spontaneous parametric down-conversion (SPDC) and spontaneous four-wave mixing are powerful nonlinear optical processes that can produce multi-photon beams of light with unique quantum properties. These processes could be leveraged to create various quantum...
PHYS.ORG
New method realize ohmic contacts in n-type MoS₂ transistors at cryogenic temperatures
Semiconducting transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) are a class of layered materials exhibiting unique optoelectronic properties that could be leveraged to develop transistors, sensors and other nanoelectronics. Despite their advantages, creating robust ohmic...
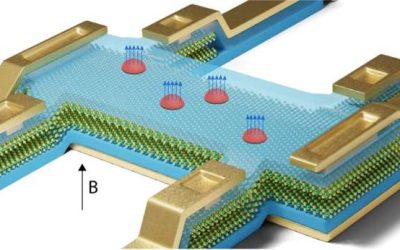
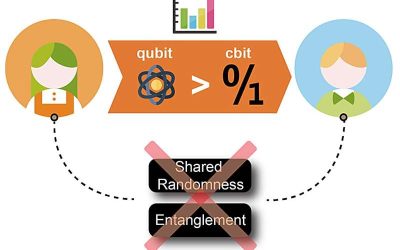
Experiment realizes quantum advantage in data storage with a photonic quantum processor
In recent years, quantum physicists and engineers have been trying to develop quantum computer processors that perform better than classical computers on some tasks. Yet conclusive demonstrations proving that quantum systems perform better than their classical...
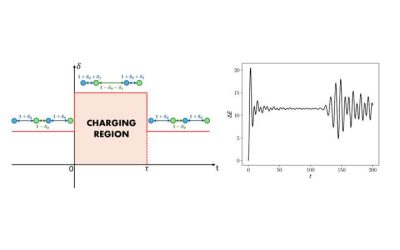
New spin quantum battery can be charged without an external field
Over the past few years, some researchers have been working on alternative energy storage systems that leverage the principles of quantum mechanics. These systems, known as quantum batteries, could be more efficient and compact than conventional battery technologies,...
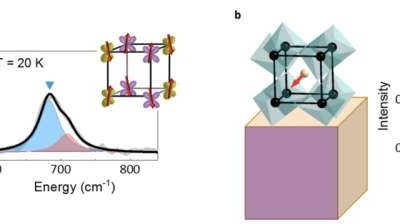
Promising strategy leverages atomic displacements to control quantum properties of a vanadate perovskite
Perovskites, materials with a crystal structure that mirrors that of the mineral calcium titanate CaTiO₃, exhibit properties that are advantageous for developing various technologies. For instance, they have proved promising for designing photovoltaic (PV) systems and...
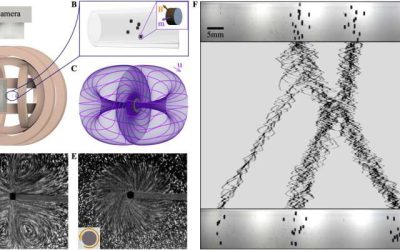
Tiny rotating particles create vorticity in viscous fluids, yielding fascinating new behaviors
Vorticity, a measure of the local rotation or swirling motion in a fluid, has long been studied by physicists and mathematicians. The dynamics of vorticity is governed by the famed Navier-Stokes equations, which tell us that vorticity is produced by the passage of...
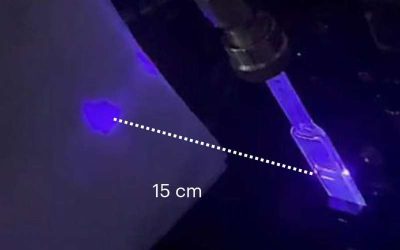
New blue light-emitting lasers leverage low-toxicity colloidal quantum dots
Blue lasers, lasers that emit a light beam with a wavelength between 400 nm and 500 nm, are key components of various technologies, ranging from high-resolution displays to printers, medical imaging tools and data storage solutions. A key advantage of these lasers is...
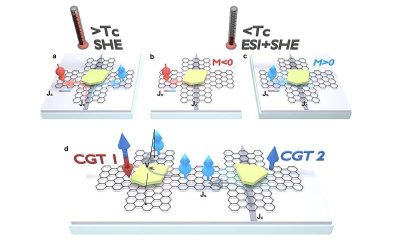
2D graphene spin valve leverages van der Waals magnet proximity for efficient spintronics
Graphene, particularly in its purest form, has long been considered a promising material for developing spintronic devices. These devices leverage the intrinsic angular momentum (i.e., spin), as opposed to the charge, of electrons to transmit and process data.
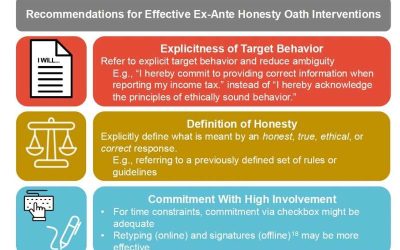
Study explores the effectiveness of honesty oath for reducing dishonest behaviors
Over the past decades, psychologists and policymakers have been trying to devise interventions that could dissuade individuals from engaging in dishonest social behaviors, such as tax evasion or fraud. One promising strategy they identified entails asking people to...
New family of optimized magnetic fields could display enhanced fusion plasma confinement
Physicists have been trying to design fusion reactors, technologies that can generate energy via nuclear fusion processes, for decades. The successful realization of fusion reactors relies on the ability to effectively confine charged particles with magnetic fields,...