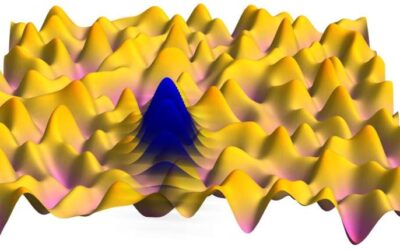
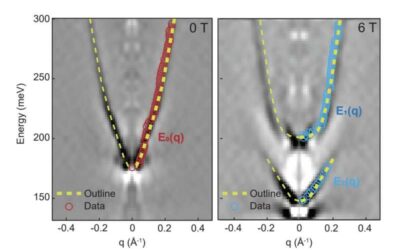
Researchers at Harvard University, Sabanci University, and Peking University recently gathered findings that could shed light on the origin of the high-temperature absorption peaks observed in strange metals, a class of materials exhibiting unusual electronic...
PHYS.ORG
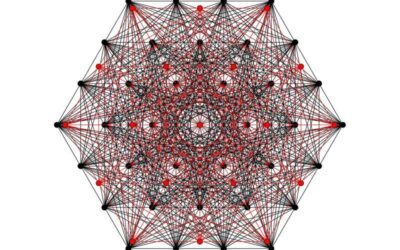
A framework to construct quantum spherical codes
To reliably perform complex, large-scale calculations, computing systems rely on so-called error correction schemes, techniques designed to protect information against errors. These techniques are perhaps even more essential when it comes to quantum computers, devices...
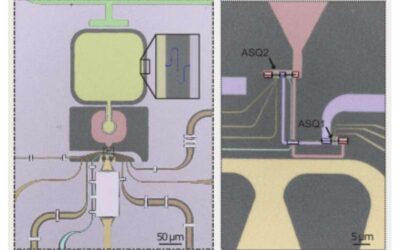
The tunable coupling of two distant superconducting spin qubits
Quantum computers, computing devices that leverage the principles of quantum mechanics, could outperform classical computing on some complex optimization and processing tasks. In quantum computers, classical units of information (bits), which can either have a value...
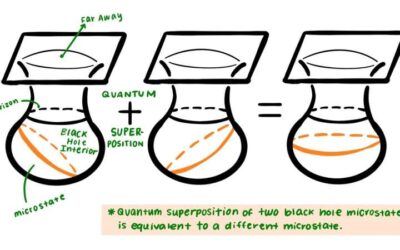
A model outlining the microscopic origin of black hole entropy
Black holes are intriguing astronomical objects that have a gravitational pull so strong that it prevents any object and even light from escaping. While black holes have been the topic of numerous astrophysical studies, their origins and underlying physics remain...
Researchers realize multiphoton electron emission with non-classical light
Strong field quantum optics is a rapidly emerging research topic, which merges elements of non-linear photoemission rooted in strong field physics with the well-established realm of quantum optics. While the distribution of light particles (i.e., photons) has been...
The observation of a Spin Berry curvature-enhanced orbital Zeeman effect in a kagome metal
In solid materials, magnetism generally originates from the alignment of electron spins. For instance, in the ferromagnet iron, the overall net magnetization is prompted by the alignment of spins in the same direction.
Study sheds light on the origin of elasticity in glasses and gels
Glasses and gels are two different types of solid materials that are commonly used in a wide range of settings. Despite their markedly different compositions, these distinct materials share some similar properties, for instance, they exhibit rigidity without a...
The BREAD Collaboration is searching for dark photons using a coaxial dish antenna
Approximately 80% of the matter in the universe is predicted to be so-called "dark matter," which does not emit, reflect, or absorb light and thus cannot be directly detected using conventional experimental techniques.
Generating graph states of atomic ensembles via photon-mediated entanglement
Graph states, a class of entangled quantum states that can be represented by graphs, have been the topic of numerous recent physics studies, due to their intriguing properties. These unique properties could make them particularly promising for quantum computing...
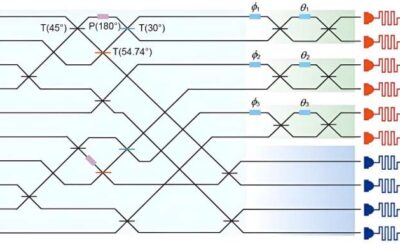
Demonstration of heralded three-photon entanglement on a photonic chip
Photonic quantum computers are computational tools that leverage quantum physics and utilize particles of light (i.e., photons) as units of information processing. These computers could eventually outperform conventional quantum computers in terms of speed, while also...