Conical structures can have advantageous applications in a variety of fields, ranging from robotics to civil engineering. Studies have found that conical shells made of liquid crystal elastomer films can be effective lifters; devices that can generate thrust for...
PHYS.ORG
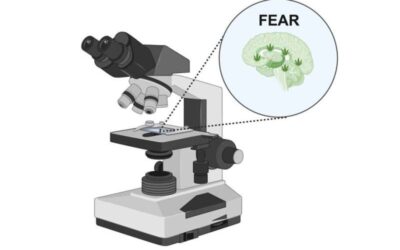
Study unveils a cortico-amygdala neural substrate supporting fear extinction via endocannabinoids
Endogenous cannabinoids, or endocannabinoids for short, are lipid-based neurotransmitters known to support various physiological processes. Recent studies have hinted at the role of these neurotransmitters in so-called fear extinction, the process through which fear...
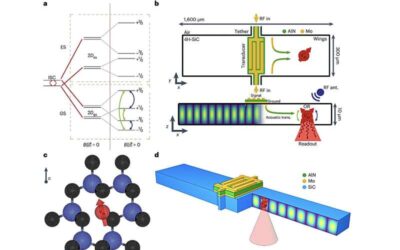
A strategy for the spin-acoustic control of silicon vacancies in a 4H silicon carbide-based bulk acoustic resonator
Bulk acoustic resonators—stacked material structures inside which acoustic waves resonate—can be used to amplify sounds or filter out undesired noise. These resonators have found wide use in today's RF telecommunication, like Front-End Modules (FEM) in iPhones. They...
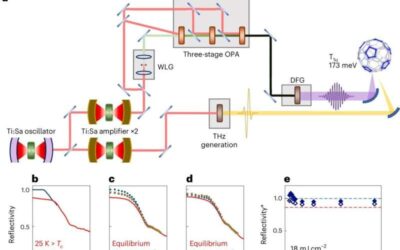
A strategy to enhance the light-driven superconductivity of K₃C₆₀
Superconductivity is the ability of some materials to conduct a direct electrical current (DC) with almost no resistance. This property is highly sought after and favorable for various technological applications, as it could boost the performance of different...
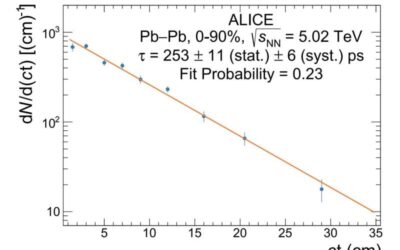
A new highly precise measurement of the hypertriton lifetime
A hypertriton is a tritium nucleus in which a neutron is replaced by a so-called Lambda hyperon. This type of hypernucleus was first discovered in the 1950s has since been the key focus of numerous studies.
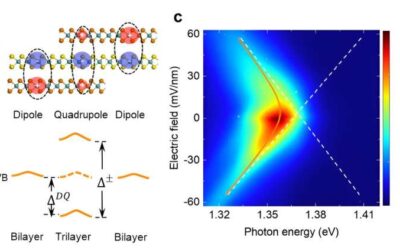
Recent manipulations of excitons in moiré superlattices
Light can excite electron and hole pairs inside semiconducting materials. If the attraction between a negatively charged electron and a positively charged hole (the antiparticle of electron in solid state physics) is strong, they stay bound together, forming states...
Theoretical study shows that Kerr black holes could amplify new physics
Black holes are regions in space characterized by extremely strong gravity, which prevents all matter and electromagnetic waves from escaping it. These fascinating cosmic bodies have been the focus of countless research studies, yet their intricate physical nuances...
A model probing the connection between entangled particles and wormholes in general relativity
Quantum entanglement is a physical process through which pairs of particles become connected and remain so even when separated by vast distances. This fascinating phenomenon has been the focus of numerous research studies, due to its mysterious nature and promising...
Researchers uncover unconventional charge carriers in a triangular-lattice Mott insulator
Mott insulators are a peculiar class of materials with structures that should theoretically conduct electricity, but that are instead insulators. These materials contain strongly correlated electrons, which can generate highly entangled many-body states marked by...
Study estimates the energy costs of information processing in biological systems
The behaviors, physiology and existence of living organisms is supported by countless biological processes, which entail the communication between cells and other molecular components. These molecular components are known to transmit information to each other in...