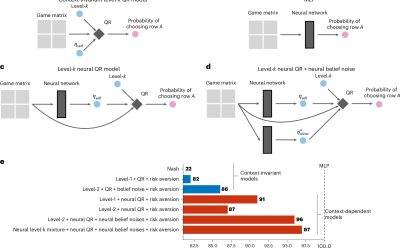
Throughout their everyday lives, humans are typically required to make a wide range of decisions, which can impact their well-being, health, social connections, and finances. Understanding the human decision-making processes is a key objective of many behavioral...
PHYS.ORG
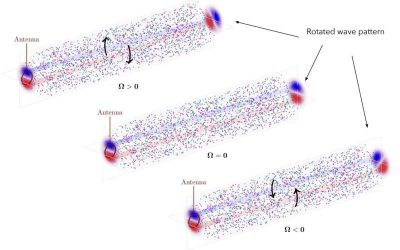
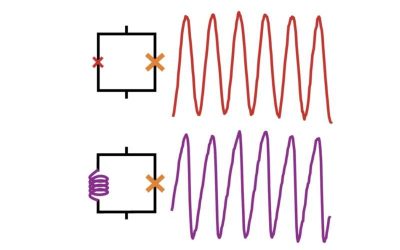
Physicists observe image rotation in plasma
Light sometimes appears to be "dragged" by the motion of the medium through which it is traveling. This phenomenon, referred to as "light dragging," is typically imperceptible when light is traveling in most widely available materials, as the movement is significantly...
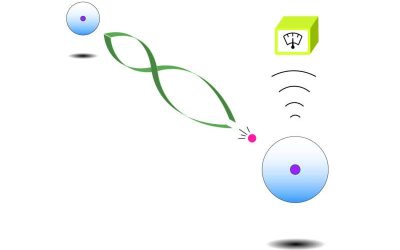
An approach to realize heralded photon storage in a Rydberg superatom
Quantum technologies, systems that operate leveraging quantum mechanical effects, have the potential to outperform classical technologies in some specific tasks. Over the past decades, some researchers have also been trying to realize quantum networks, systems...
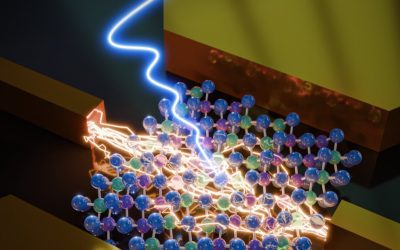
TaIrTe₄ photodetectors show promise for highly sensitive room-temperature THz sensing
Terahertz radiation (THz), electromagnetic radiation with frequencies ranging between 0.1 and 10 THz, could be leveraged to develop various new technologies, including imaging and communication systems. So far, however, a lack of fast and sensitive detectors that can...
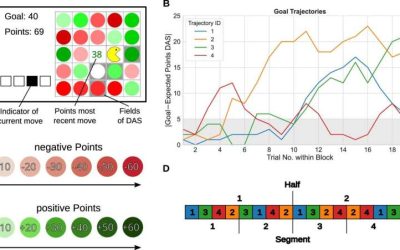
Humans tend to repeat familiar actions when making sequential decisions, even when better options exist
Behavioral scientists have been trying to uncover the patterns that humans follow when making decisions for decades. The insights gathered as part of their studies can help shape public policies and interventions aimed at prompting people to make better decisions,...
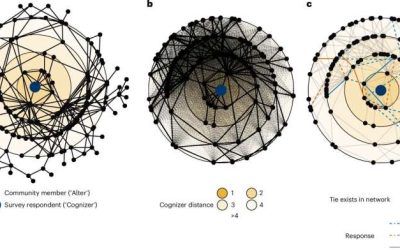
Biases shape how people mentally represent social ties in their community, study suggests
Throughout the course of their lives, humans are known to build social ties with various other individuals in their community. Past neuroscience and psychology studies suggest that as humans form bonds with others, they also mentally represent them in their minds,...
Snails get stressed: Invertebrate model sheds light on biological basis of anxiety
Anxiety, the psychological and physiological state characterized by an anticipation of potential threats and a heightened sense of vigilance, is regularly experienced by many humans worldwide. Research suggests that anxiety is a behavioral consequence of stress,...
Twisted trilayer graphene shows high kinetic inductance
Superconductivity is an advantageous physical phenomenon observed in some materials, which entails an electrical resistance of zero below specific critical temperatures. This phenomenon is known to arise following the formation of so-called Cooper pairs (i.e., pairs...
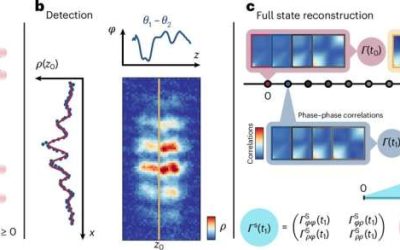
A new approach to probing Landauer’s principle in the quantum many-body regime
Landauer's principle is a thermodynamics concept also relevant in information theory, which states that erasing one bit of information from an information system results in the dissipation of at least a specific amount (i.e., kBTln2) of energy. This principle has...
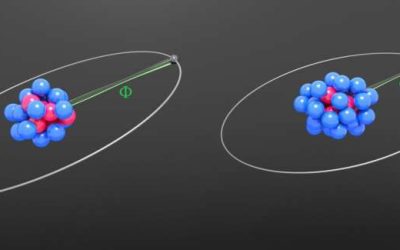
Study tightens King plot-based constraints on hypothetical fifth force
While the Standard Model (SM) describes all known fundamental particles and many of the interactions between them, it fails to explain dark matter, dark energy and the apparent asymmetry between matter and antimatter in the universe. Over the past decades, physicists...