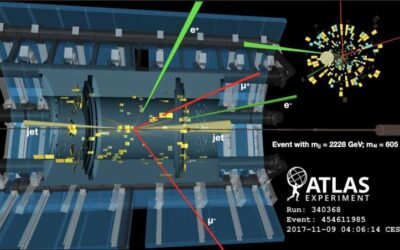
The ATLAS collaboration, the large research consortium involved in analyzing data collected by the ATLAS particle collider at CERN, recently observed the electroweak production of two Z bosons and two jets. This crucial observation, presented in Nature Physics,...
PHYS.ORG
The SNO+ collaboration gathers the first evidence of antineutrinos in a water Cherenkov detector
Antineutrinos, the antimatter counterpart of neutrinos, have an almost non-existent mass and charge, and almost never interact with other particles, which makes them particularly difficult to detect. Physicists have been studying neutrinos from reactors for many...
A universal protocol that inverts the evolution of a qubit with a high probability of success
Researchers at the Institute for Quantum Optics and Quantum Information (IQOQI) in Vienna recently devised a universal mechanism to invert the evolution of a qubit with a high probability of success. This protocol, outlined in Physical Review Letters, can...
The modulation of a single-molecule electron source using light
Researchers at University of Tokyo, JTS PRESTO, Ludwig Maximilians Universität and Kindai University recently demonstrated the modulation of an electron source by applying laser light to a single fullerene molecule. Their study, featured in Physical Review...
A robust quantum memory that stores information in a trapped-ion quantum network
Researchers at University of Oxford have recently created a quantum memory within a trapped-ion quantum network node. Their unique memory design, introduced in a paper in Physical Review Letters, has been found to be extremely robust, meaning that it could store...
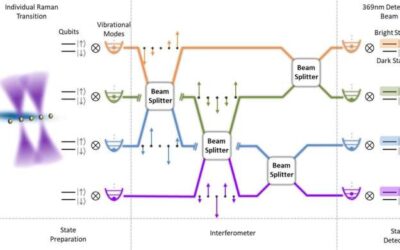
A scalable and programmable quantum phononic processor based on trapped ions
Quantum computing systems have the potential to outperform classical computers on some tasks, helping to solve complex real-world problems in shorter times. Research teams worldwide have thus been trying to realize this quantum advantage over traditional computers, by...
Study uncovers the fundamental mechanisms underlying the formation of polarons in 2D atomic crystals
Polarons are localized quasiparticles that result from the interaction between fermionic particles and bosonic fields. Specifically, polarons are formed when individual electrons in crystals distort their surrounding atomic lattice, producing composite objects that...
The experimental observation of quantum avalanches in a many-body localized system
Strongly correlated systems are systems made of particles that strongly interact with one another, to such an extent that their individual behavior depends on the behavior of all other particles in the system. In states that are far from equilibrium, these systems can...
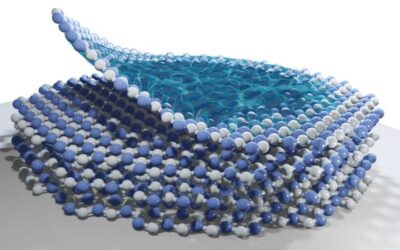
Study identifies a new synthesis technique to attain monolayer honeycomb SiC
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a hard crystalline compound of silicon and carbon that rarely occurs in nature and is generally synthetically produced. In addition to being used to create ceramic plates, bulletproof vests and other commercial products, SiC is a...
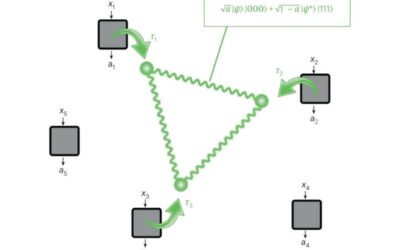
A framework to self-test all entangled states using quantum networks
Self-testing is a promising method to infer the physics underlying specific quantum experiments using only collected measurements. While this method can be used to examine bipartite pure entangled states, so far it could only be applied to limited kinds of quantum...