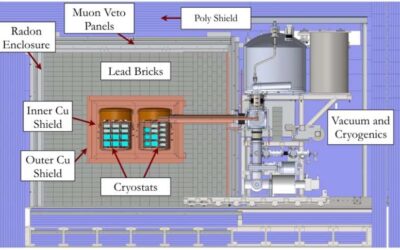
For more than half a decade, the Majorana Collaboration, a large consortium of researchers from different universities worldwide, have been trying to observe neutrinoless double-beta decay, one of the rarest forms of radioactive decay. This was done using the Majorana...
PHYS.ORG
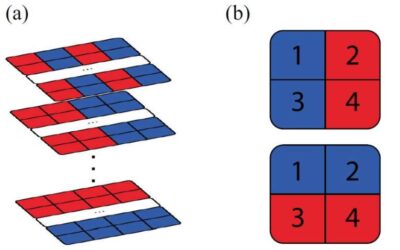
The experimental realization of quantum overlapping tomography
Quantum tomography is a process that involves the reconstruction and characterization of a quantum state using a series of collected measurements. Over the past few years, many physicists have been trying to use this process to learn more about quantum states, as this...
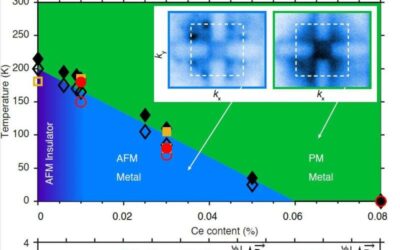
Study unveils an antiferromagnetic metal phase in an electron-doped rare-earth nickelate
Researchers at Harvard University, the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Arizona State University, and other institutes in the United States have recently observed an antiferromagnetic metal phase in electron-doped NdNiO3 a material known to be a...
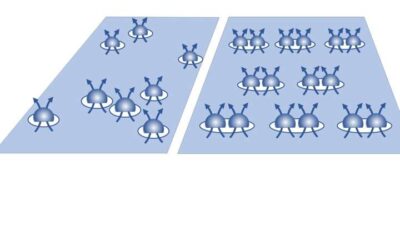
Researchers observe a bubble phase of composite fermions
Strong interactions between particles in physical systems can result in various highly correlated ground states. These states and the strong correlations underpinning them have been extensively explored in recent years.
A multi-turn energy recovery accelerator that achieves high beam power with lower power consumption
Particle accelerators are devices that use electromagnetic fields to speed up particles and collide them together or against a specific target. These devices are widely used by physicists to study particles, the forces that drive them and interactions between them.
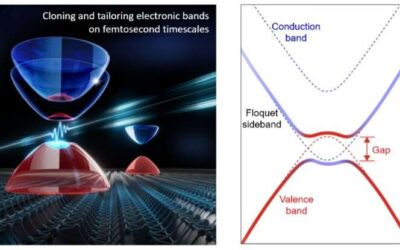
Floquet band engineering in black phosphorus
Physicists have been trying to identify reliable strategies to manipulate quantum states in solid-state materials, cold atoms and other systems, as this could inform the development of new technologies. One of these strategies is Floquet engineering, which entails the...
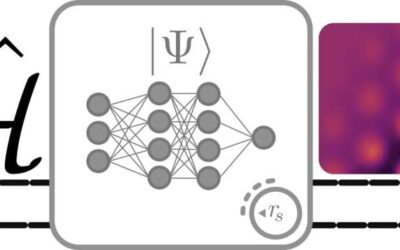
An extension of FermiNet to discover quantum phase transitions
Architectures based on artificial neural networks (ANNs) have proved to be very helpful in research settings, as they can quickly analyze vast amounts of data and make accurate predictions. In 2020, Google's British AI subsidiary DeepMind used a new ANN architecture...
Study unveils a large tunable drag response between a normal conductor and a superconductor
The Coloumb drag is a phenomenon that affects two electronic circuits, whereby a charge current in one circuit induces a responsive current in a neighboring circuit solely through so-called Coloumb interactions. These are electrostatic interactions between electric...
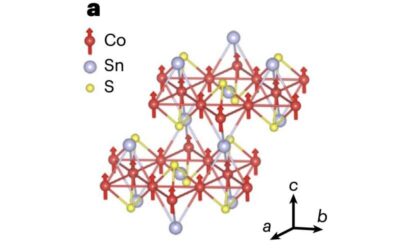
Modulating magnetism in a Weyl semi-metal using current-assisted domain wall motion
Spintronic devices are emerging technologies that exploit the intrinsic spin of electrons to store and process data. These technologies have the potential to outperform conventional electronics both in terms of speed and energy-efficiency.
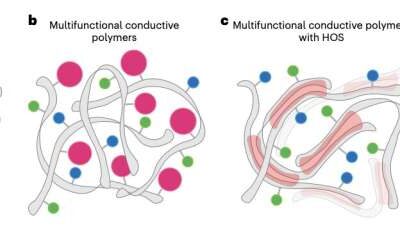
A method to change the mechanical and transport properties of conductive polymers
Conductive polymers, synthetic substances with large molecules that can conduct electricity, can have a broad range of valuable applications. For instance, they have been used to create sensors, light-emitting diodes, photovoltaics and various other devices.