Embezzlement of entanglement is an exotic phenomenon in quantum information science, describing the possibility of extracting entanglement from a resource system without changing its quantum state. In this context, the resource systems play the role of a catalyst,...
PHYS.ORG
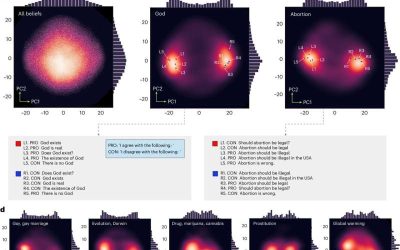
LLMs delve into online debates to create a detailed map of human beliefs
Large language models (LLMs), such as the model underpinning the functioning of the well-known conversational platform ChatGPT, have proved to be very promising for summarizing and generating written texts. However, they could also be interesting tools for conducting...
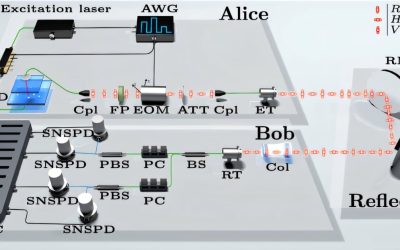
True single-photon source boosts secure key rates in quantum key distribution systems
Quantum key distribution (QKD), a cryptographic technique rooted in quantum physics principles, has shown significant potential for enhancing the security of communications. This technique enables the transmission of encryption keys using quantum states of photons or...
Atom tweezer arrays reveal how phase transitions unfold in mesoscopic systems
As the number of particles in a physical system increases, its properties can change and different phase transitions (i.e., shifts into different phases of matter) can take place. Microscopic systems (i.e., containing only a few particles) and macroscopic ones (i.e.,...
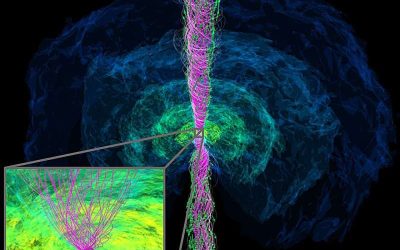
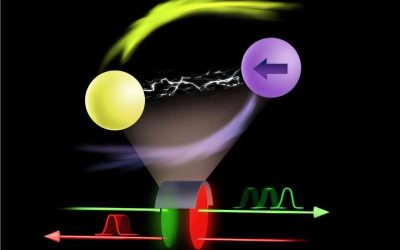
Simulation reveals emergence of jet from binary neutron star merger followed by black hole formation
Binary neutron star mergers, cosmic collisions between two very dense stellar remnants made up predominantly of neutrons, have been the topic of numerous astrophysics studies due to their fascinating underlying physics and their possible cosmological outcomes. Most...
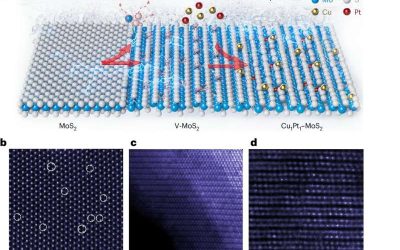
New approach reversibly configures single and heteronuclear dual-atom catalysts on MoS₂ substrate
Single-atom catalysts (SACs) are materials consisting of individual metal atoms dispersed on a substrate (i.e., supporting surface). Recent studies have highlighted the promise of these catalysts for the efficient conversion and storage of energy, particularly when...
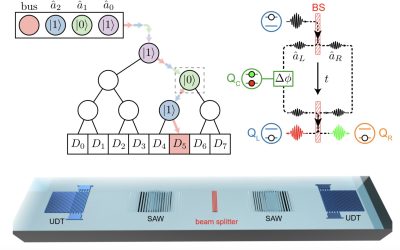
A quantum random access memory based on transmon-controlled phonon routers
Recent technological advances have opened new exciting possibilities for the development of cutting-edge quantum devices, including quantum random access memory (QRAM) systems. These are memory architectures specifically meant to be integrated inside quantum...
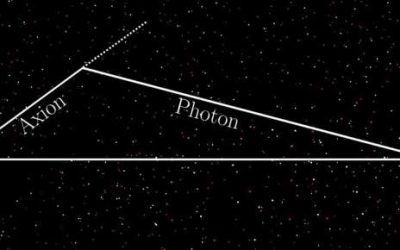
Searching for axions by analyzing X-ray observations of entire galaxies
The ongoing search for dark matter, the elusive type of matter that does not emit, absorb or reflect light and is estimated to account for most of the universe's mass, has not yet yielded conclusive results. Axions, hypothetical elementary particles that were first...
Nonreciprocal light speed control achieved using cavity magnonics device
The reliable manipulation of the speed at which light travels through objects could have valuable implications for the development of various advanced technologies, including high-speed communication systems and quantum information processing devices. Conventional...
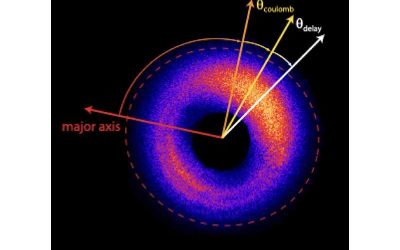
Phase-resolved attoclock precisely measures electron tunneling time
When placed under a powerful laser field (i.e., under strong-field ionization), electrons can temporarily cross the so-called quantum tunneling barrier, an energy barrier that they would typically be unable to overcome. This quantum mechanics phenomenon, known as...