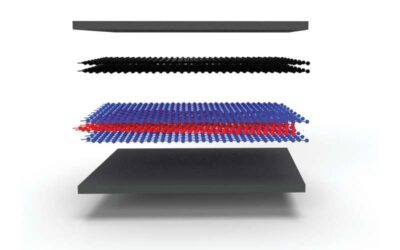
In recent years, physicists and material scientists have uncovered several new platforms for studying correlated phases of matter, such as superconductivity and the correlated insulator phase. Among them is magic-angle twisted trilayer graphene, a superconductor...
PHYS.ORG
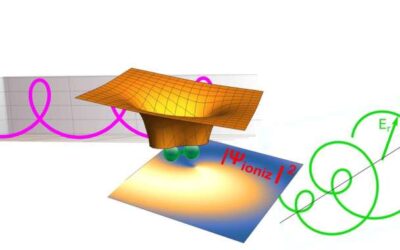
A fully optical attoclock to image tunnelling wavepackets
Attoclocks, or attosecond clocks, are instruments that can measure time intervals on the attosecond scale by measuring the time it takes for electrons to tunnel out of atoms. The attosecond procedure was first introduced by a research team led by Ursula Keller in...
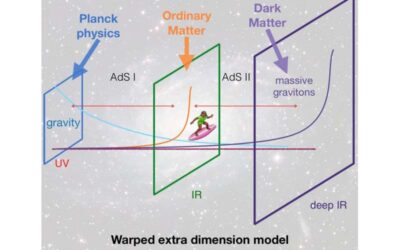
Could massive gravitons be viable dark matter candidates?
Today, many research teams worldwide are trying to detect dark matter, an invisible substance that is believed to account for most of the matter in the universe. As does not reflect or emit light, its presence has been indirectly revealed via its gravitational...
The experimental demonstration of topological dissipation in photonic resonators
So far, physicists have primarily studied topological phases in conservatively coupled systems. These are systems with dynamics that do not dissipate and a phase space that does not shrink over time. They are in stark contrast with dissipative systems, which are...
Researchers design holographic lenses based on plasma
Holograms are three-dimensional (3D) images produced by interfering beams of light that reflect physical objects or photographs. In recent years, they were introduced in a variety of settings, for instance to enhance employee training or create more engaging art.
The IceCube Collaboration sets the most restrictive constraints on relic magnetic monopoles from the early universe
Recent technological advances have enabled the development of increasingly advanced telescope and astrophysical instruments. This includes the IceCube telescope, which was originally built to detect and examine high-energy neutrinos in the universe.
Physicists test real quantum theory in an optical quantum network
Quantum theory was originally formulated using complex numbers. Nonetheless, when replying to a letter by Hendrik Lorenz, Erwin Schrödinger (one of its founding fathers), wrote: "Using complex numbers in quantum theory is unpleasant and should be objected to. The wave...
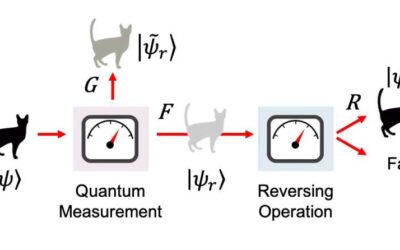
Study redefines what information is important in quantum measurements
Researchers at Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) have recently tried to capture the interplay between different types of information that are important while collecting quantum measurements, namely information gain, disturbance and reversibility. Their...
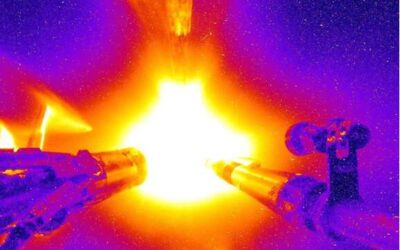
New studies highlight the potential of self-heating plasmas for fusion energy
Most energy-producing technologies used today are unsustainable, as they cause significant damage to our planet's natural environment. In recent years, scientists worldwide have thus been trying to devise alternative energy solutions that take advantage of abundant...
Examining the results of new dark matter searches by the PandaX-4T and ADMX collaborations
Physicists have predicted the existence of dark matter, a material that does not absorb, emit or reflect light, for decades. While there is now significant evidence hinting to the existence of dark matter in the universe, as it was never directed detected before its...