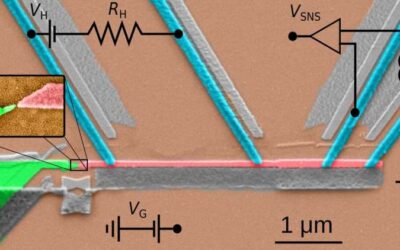
While many research teams worldwide are trying to develop highly performing quantum computers, some are working on tools to control the flow of heat inside of them. Just like conventional computers, in fact, quantum computers can heat up significantly as they are...
PHYS.ORG
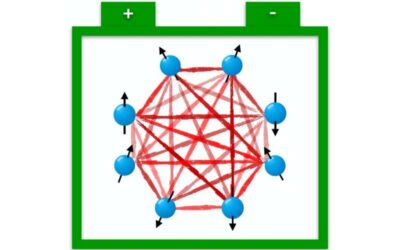
Using the SYK model to examine the fast-charging process of quantum batteries
The Sachdev-Ye-Kitaev (SYK) model, an exactly solvable model devised by Subir Sachdev and Jinwu Ye, has recently proved useful for understanding the characteristics of different types of matter. As it describes quantum matter without quasiparticles and is...
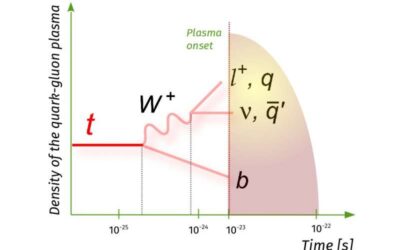
The first evidence of top quark production in nucleus-nucleus collisions
The Compact Muon Solenoid (CMS) Collaboration, a large group of researchers from different institutes worldwide, has recently gathered the very first evidence of top quark production in nucleus-nucleus collisions. Their work, outlined in a paper published in Physical...
Study demonstrates the quenching of an antiferromagnet into high resistivity states
Antiferromagnetism is a type of magnetism in which parallel but opposing spins occur spontaneously within a material. Antiferromagnets, materials that exhibit antiferromagnetism, have advantageous characteristics that make them particularly promising for fabricating...
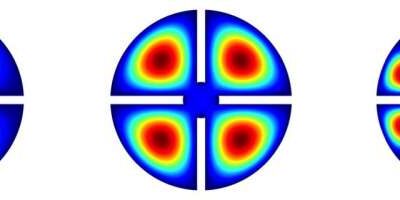
Searching for invisible axion dark matter with a new multiple-cell cavity haloscope
Over the past few decades, many experimental physicists have been probing the existence of particles called axions, which would result from a specific mechanism that they think could explain the contradiction between theories and experiments describing a fundamental...
New constraints on alternative gravity theories that could inform dark matter research
While particle theories are currently the most favored explanations for dark mater, physicists have still been unable to detect dark matter particles in ways that would confirm or contradict these theories. Some theorists have thus been exploring new theories of...
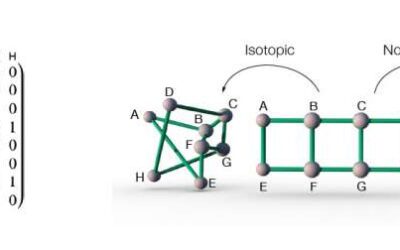
Network isotopy: A framework to study the 3-D layouts of physical networks
The structure and functions of many physical networks, including the human brain, the vascular system and other biological networks, often depend on their three-dimensional and geometrical layout. Distinguishing between physical networks with identical connections but...
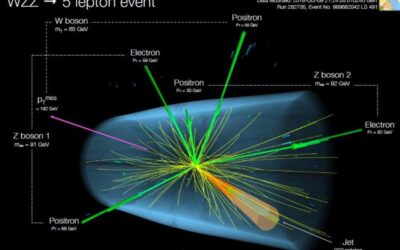
Triple threat: The first observation of three massive gauge bosons produced in proton-proton collisions
The Standard Model, the most exhaustive existing theory outlining fundamental particle interactions, predicts the existence of what are known as triboson interactions. These interactions are processes in which three-gauge bosons are simultaneously produced from one...
Researchers observe what could be the first hints of dark bosons
Extremely light and weakly interacting particles may play a crucial role in cosmology and in the ongoing search for dark matter. Unfortunately, however, these particles have so far proved very difficult to detect using existing high-energy colliders. Researchers...
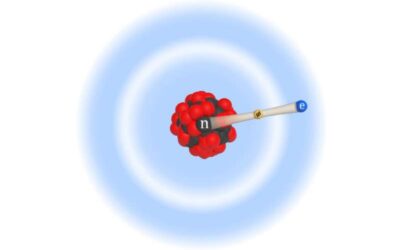
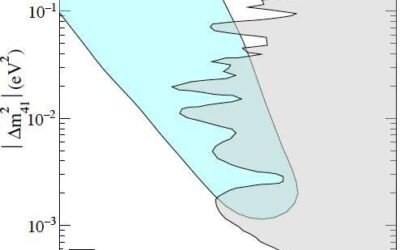
Searching for sub-eV sterile neutrinos using two highly sensitive detectors
The standard model of particle physics only accounts for 20% of matter in the universe. Physicists have theorized that the remaining 80% is made up by so-called dark matter, which consists of particles that do not emit, absorb or reflect light and thus cannot be...