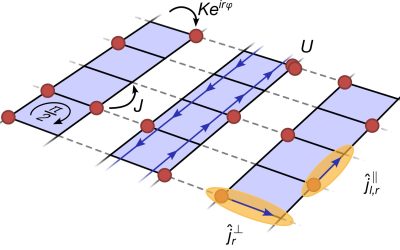
When exposed to periodic driving, which is the time-dependent manipulation of a system's parameters, quantum systems can exhibit interesting new phases of matter that are not present in time-independent (i.e., static) conditions. Among other things, periodic driving...
PHYS.ORG
Using a fermionic neural network to find the ground state of fractional quantum Hall liquids
When two-dimensional electron systems are subjected to magnetic fields at low temperatures, they can exhibit interesting states of matter, such as fractional quantum Hall liquids. These are exotic states of matter characterized by fractionalized excitations and the...
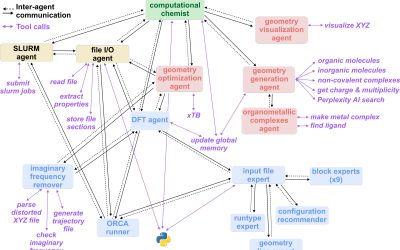
Conversational agent can create executable quantum chemistry workflows
Artificial intelligence (AI) agents and large-language models (LLMs), such as the model underpinning OpenAI's conversational platform ChatGPT, are now widely used by people worldwide, both in informal and professional settings. Over the past decade or so, some of...
TeV halos could be a common feature of middle-aged pulsars, study shows
Pulsars are rapidly rotating neutron stars that emit regular radio wave pulses and beams of magnetic radiation, which can sometimes be detected from Earth. These pulsating stars are dense remnants of massive stars whose life terminated in a supernova explosion.
Astrobee learns to transport soft cargo: Open-source simulator models real ISS challenges
Astrobee is a free-flying robotic system developed by NASA that is made up of three distinct cube-shaped robots. This system was originally designed to help astronauts who are working at the International Space Station (ISS) by automating some of their routine manual...
Nanoparticle-cell interface enables electromagnetic wireless programming of mammalian transgene expression
Recent technological advances are fueling the development of cutting-edge technologies that can monitor and control physiological processes with high precision. These include devices that could control the expression of genes within living organisms, without requiring...
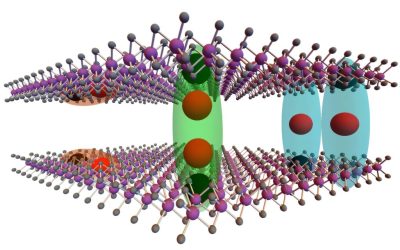
Two distinct exciton states observed in 2H stacked bilayer molybdenum diselenide
Two-dimensional (2D) materials have proved to be a promising platform for studying exotic quasiparticles, such as excitons. Excitons are bound states that emerge when an electron in a material absorbs energy and rises to a higher energy level, leaving a hole (i.e.,...
Two distinct exciton states observed in 2H stacked bilayer molybdenum diselenide
Two-dimensional (2D) materials have proved to be a promising platform for studying exotic quasiparticles, such as excitons. Excitons are bound states that emerge when an electron in a material absorbs energy and rises to a higher energy level, leaving a hole (i.e.,...
Results of the HAYSTAC Phase II search for dark matter axions
Axions, hypothetical subatomic particles that were first proposed by theoretical physicists in the late 1970s, remain among the most promising dark matter candidates. Physics theories suggest that the interactions between these particles and regular matter are...
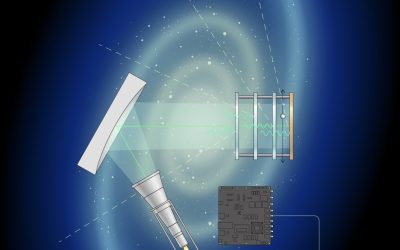
Results of the first search for dark photons using a MADMAX prototype
While many research groups worldwide have been searching for dark matter over the past decades, detecting it has so far proved very challenging, thus very little is known about its possible composition and physical properties. Two promising dark matter candidates...