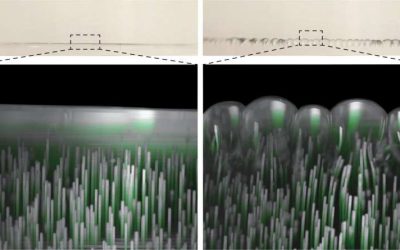
Soft viscoelastic solids are flexible materials that can return to their original shape after being stretched. Due to the unique properties driving their deformation, these materials can sometimes behave and change shape in unexpected ways.
Soft Matter
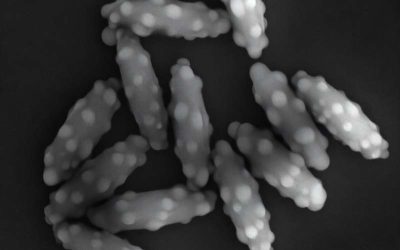
Surface roughness disrupts glass transition in colloidal ellipsoids, offering a new material design parameter
The so-called glass transition is the process by which some liquid-like materials become solid-like, without forming a crystalline structure. In contrast to conventional solid materials, which exhibit an orderly atom arrangement, glass is characterized by a disordered...
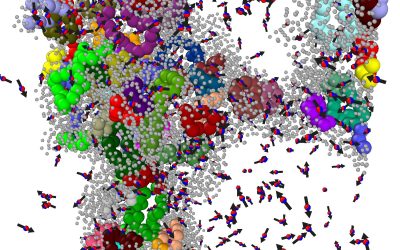
Superionic compound with liquid-like dynamics shows promise as solid-state battery electrolyte
Superionic materials are a class of materials that simultaneously present properties that are characteristic of solids and liquids. Essentially, a set of ions in these materials exhibits liquid-like mobility, even if the materials' underlying atomic structure...
Active particles reorganize 3D gels into denser porous structures, study shows
Colloidal gels are complex systems made up of microscopic particles dispersed in a liquid, ultimately producing a semi-solid network. These materials have unique and advantageous properties that can be tuned using external forces, which have been the focus of various...
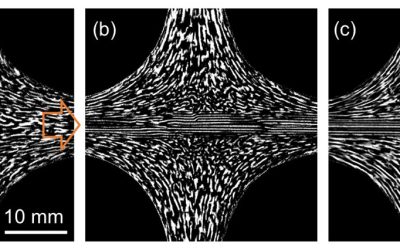
Physicists introduce approach to control wave patterns via fluid flows
The reliable control of traveling waves emerging from the coupling of oscillations and diffusion in physical, chemical and biological systems is a long-standing challenge within the physics community. Effective approaches to control these waves help to improve the...
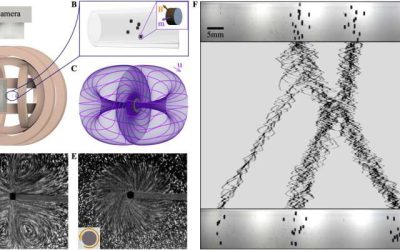
Tiny rotating particles create vorticity in viscous fluids, yielding fascinating new behaviors
Vorticity, a measure of the local rotation or swirling motion in a fluid, has long been studied by physicists and mathematicians. The dynamics of vorticity is governed by the famed Navier-Stokes equations, which tell us that vorticity is produced by the passage of...
A new robotic platform to reproduce and study complex ciliary behavior
Cilia are sensory structures extending from the surface of some cells. These hair-like structures are known to contribute to the sensorimotor capabilities of various living organisms, including humans.
Exploring what happens when different spherical objects hit the water
When an object hits a body of water vertically, it is accompanied by a strong hydrodynamic force fueled by the flow of water around it, which propels it forward. The magnitude of this force is known to vary depending on the mass of the object hitting the water.
Study sheds light on the origin of elasticity in glasses and gels
Glasses and gels are two different types of solid materials that are commonly used in a wide range of settings. Despite their markedly different compositions, these distinct materials share some similar properties, for instance, they exhibit rigidity without a...
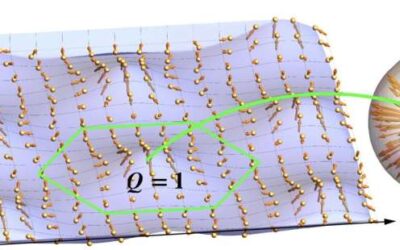
Researchers offer theoretical description of topological water wave structures
Topological wave structures are wave patterns that exhibit specific topological properties, or in other words, properties that remain unvaried under smooth deformations of a physical system. These structures, such as vortices and skyrmions, have attracted significant...