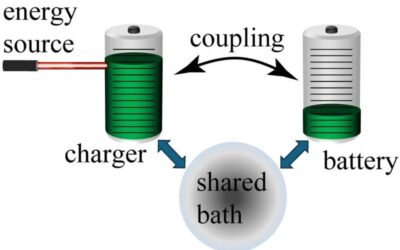
In physics, nonreciprocity occurs when a system's response varies depending on the direction in which waves or signals are propagating within it. This asymmetry arises from a break in so-called time-reversal symmetry, which essentially means that a system's processes...
Physics
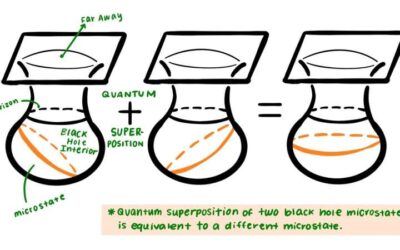
A model outlining the microscopic origin of black hole entropy
Black holes are intriguing astronomical objects that have a gravitational pull so strong that it prevents any object and even light from escaping. While black holes have been the topic of numerous astrophysical studies, their origins and underlying physics remain...
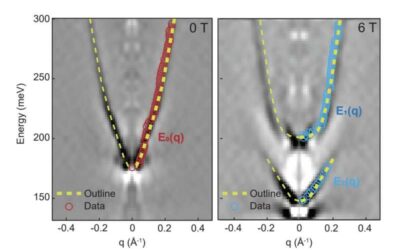
The observation of a Spin Berry curvature-enhanced orbital Zeeman effect in a kagome metal
In solid materials, magnetism generally originates from the alignment of electron spins. For instance, in the ferromagnet iron, the overall net magnetization is prompted by the alignment of spins in the same direction.
Study sheds light on the origin of elasticity in glasses and gels
Glasses and gels are two different types of solid materials that are commonly used in a wide range of settings. Despite their markedly different compositions, these distinct materials share some similar properties, for instance, they exhibit rigidity without a...
The BREAD Collaboration is searching for dark photons using a coaxial dish antenna
Approximately 80% of the matter in the universe is predicted to be so-called "dark matter," which does not emit, reflect, or absorb light and thus cannot be directly detected using conventional experimental techniques.
Generating graph states of atomic ensembles via photon-mediated entanglement
Graph states, a class of entangled quantum states that can be represented by graphs, have been the topic of numerous recent physics studies, due to their intriguing properties. These unique properties could make them particularly promising for quantum computing...
Demonstration of heralded three-photon entanglement on a photonic chip
Photonic quantum computers are computational tools that leverage quantum physics and utilize particles of light (i.e., photons) as units of information processing. These computers could eventually outperform conventional quantum computers in terms of speed, while also...
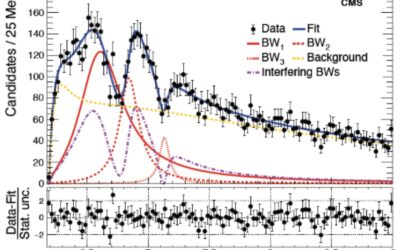
CMS Collaboration observes new all-heavy quark structures
For over a decade, the CMS Collaboration, a large team of researchers based at different institutes worldwide, has been analyzing data collected at the Compact Muon Solenoid, a general-purpose particle detector at CERN's Large Hadron Collider (LHC). This large-scale...
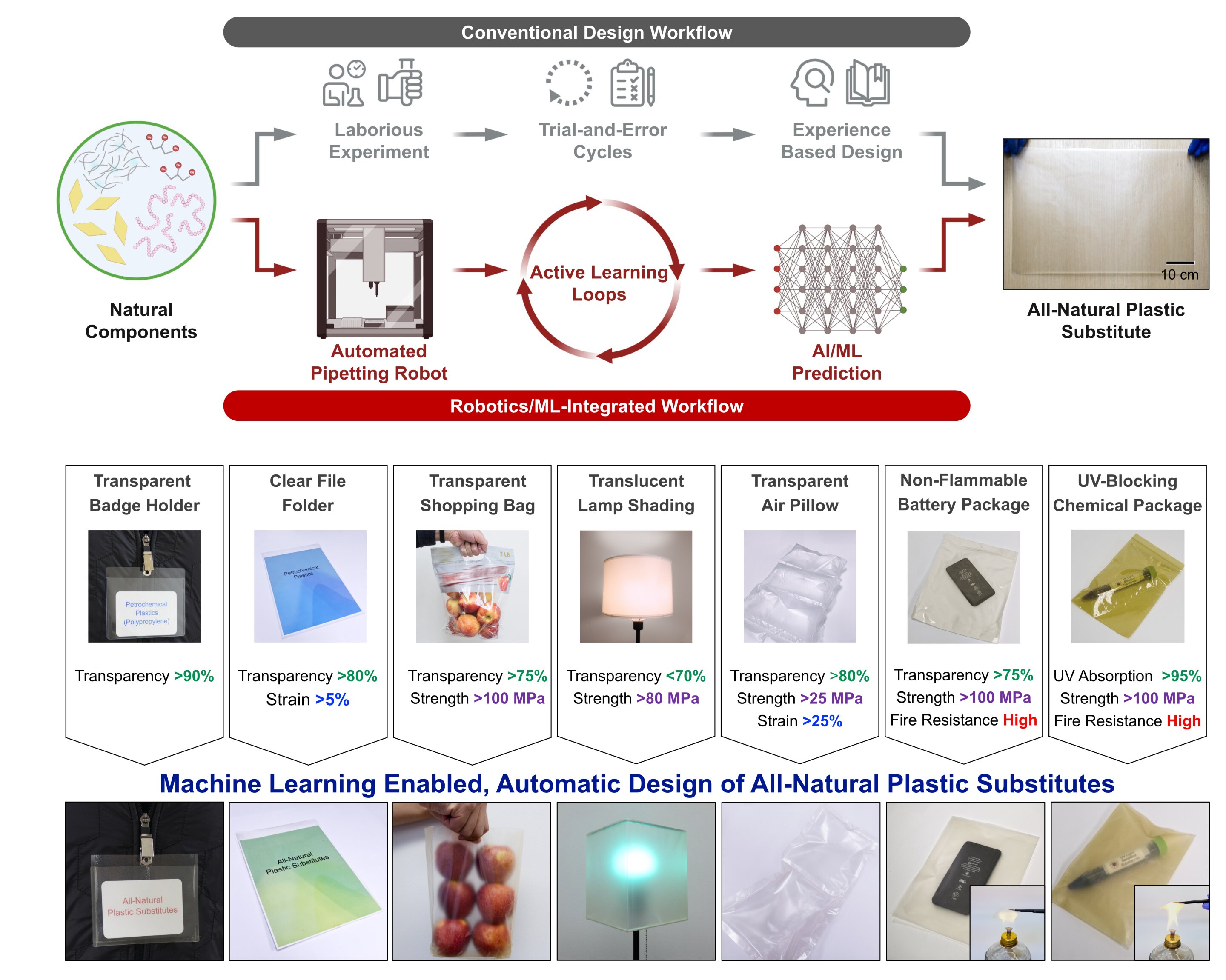
A machine learning-based approach to discover nanocomposite films for biodegradable plastic alternatives
The accumulation of plastic waste in natural environments is of utmost concern, as it is contributing to the destruction of ecosystems and is causing harm to aquatic life. In recent years, material scientists have thus been trying to identify all-natural alternatives...
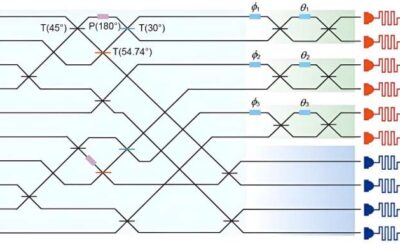
The experimental demonstration of a verifiable blind quantum computing protocol
Quantum computers, systems that process and store information leveraging quantum mechanical phenomena, could eventually outperform classical computers on numerous tasks. Among other things, these computers could allow researchers to tackle complex optimization...