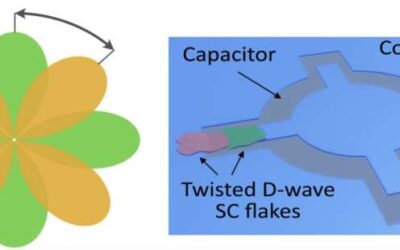
Quantum technology could outperform conventional computers on some advanced optimization and computational tasks. In recent years, physicists have been working to identify new strategies to create quantum systems and promising qubits (i.e., basic units of information...
Physics
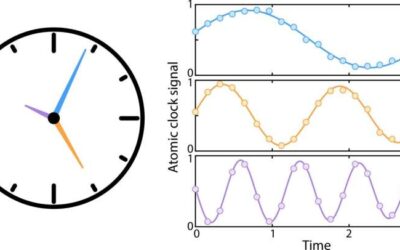
A multi-ensemble atomic clock enhanced using quantum computing tools
Atomic clocks are a class of clocks that leverage resonance frequencies of atoms to keep time with high precision. While these clocks have become increasingly advanced and accurate over the years, existing versions might not best utilize the resources they rely on to...
Researchers demonstrate multi-photon state transfer between remote superconducting nodes
Over the past few decades, quantum physicists and engineers have been trying to develop new, reliable quantum communication systems. These systems could ultimately serve as a testbed to evaluate and advance communication protocols.
Evidence that atomically thin hafnium telluride is an excitonic insulator
The condensation of excitons with non-zero momentum can give rise to so-called charge density waves (CDW). This phenomenon can prompt the transition of materials into a fascinating new quantum phase, known as an excitonic insulator.
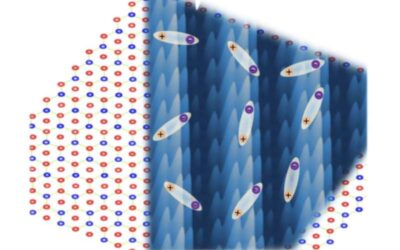
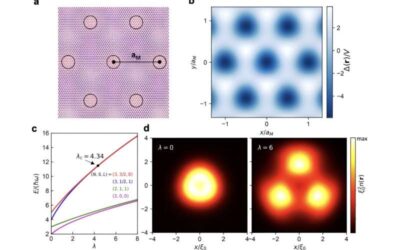
Exploring new physics arising from electron interactions in semiconductor moiré superlattices
Semiconductor moiré superlattices are fascinating material structures that have been found to be promising for studying correlated electron states and quantum physics phenomena. These structures, made up of artificial atom arrays arranged in a so-called moiré...
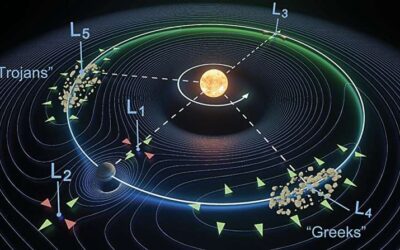
A Trojan approach to guide and trap light beams via Lagrange points
Reliably guiding and capturing optical waves is central to the functioning of various contemporary technologies, including communication and information processing systems. The most conventional approach to guide light waves leverages the total internal reflection of...
A method to fabricate long rolls of subnanocomposite dielectric polymers
Engineers and material scientists have been trying to develop increasingly advanced devices, to meet the growing needs of the electronics industry. These devices include electrostatic capacitors, devices that can store electrical energy in a dielectric between a pair...
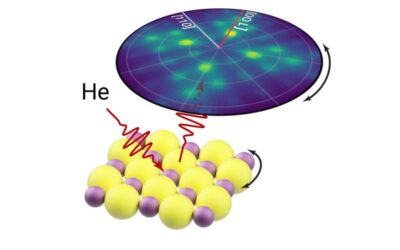
Collecting helium diffraction patterns in microscopic regions of samples
Recent scientific advancements have opened new opportunities for the close observation of physical phenomena. Researchers at University of Cambridge and University of Newcastle recently introduced a new method to measure helium atom diffraction with microscopic...
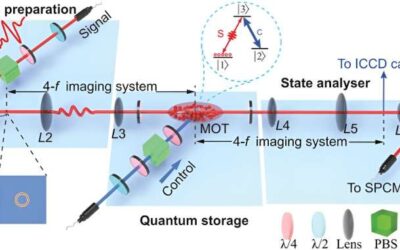
A new approach to realize highly efficient, high-dimensional quantum memories
Many physicists and engineers have been trying to develop highly efficient quantum technologies that can perform similar functions to conventional electronics leveraging quantum mechanical effects. This includes high-dimensional quantum memories, storage devices with...
Mapping the relations between Manhattan Project scientists using network science
The Manhattan Project was a top-secret program that culminated in the development of the first atomic bombs during World War 2. This covert and controversial research endeavor involved many gifted and reputable scientists, including physicist J. Robert Oppenheimer.