The Muon g-2 Collaboration is a large group of researchers at different institutes worldwide collaborating on the Muon g-2 experiment. This is a research effort aimed at exploring the interactions of muons, short-lived particles that are essentially heavy electrons,...
Physics
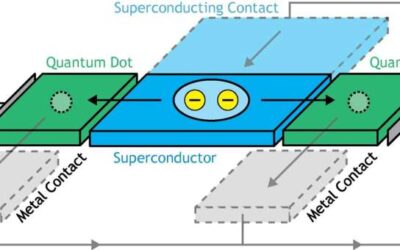
The controllable splitting of a single Cooper pair in a hybrid quantum dot system
Cooper pairs are pairs of electrons in superconducting materials that are bound to each other at low temperatures. These electron pairs are at the root of superconductivity, a state where materials have zero resistance at low temperatures due to quantum effects. As...
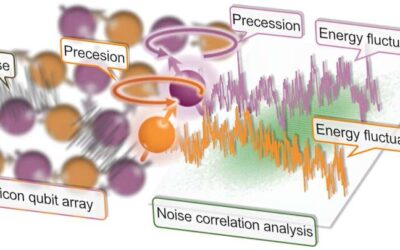
Study observes strong noise correlations between silicon qubits
To build highly performing quantum computers, researchers should be able to reliably derive information about the noise inside them, while also identifying effective strategies to suppress this noise. In recent years, significant progress has been made in this...
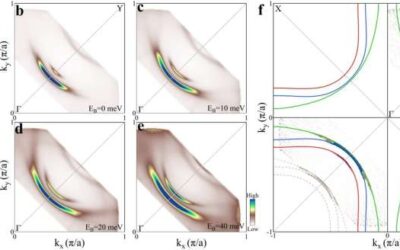
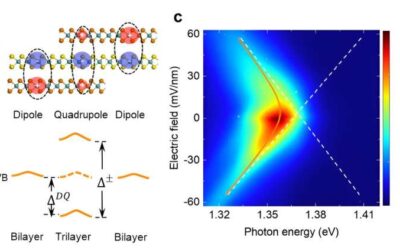
Study reveals the origin of high superconducting critical temperatures in trilayer cuprates
High-temperature cuprate superconductors are a broad class of materials that exhibit some unique characteristics. Due to their distinctive properties, these materials exhibit the highest superconducting temperatures reported to date under ambient pressure.
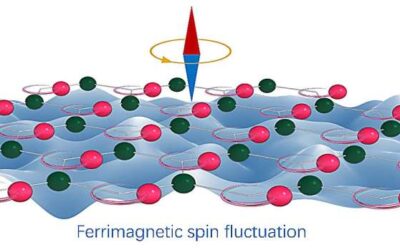
Study uncovers giant fluctuation-enhanced phonon magnetic moments in a polar antiferromagnet
Phonons, quasi-particles associated with sounds or lattice vibrations, can carry momentum and angular momentum. However, these quasi-particles are commonly considered to possess negligible magnetic moments.
A new formula to calculate the strength of thin conical structures
Conical structures can have advantageous applications in a variety of fields, ranging from robotics to civil engineering. Studies have found that conical shells made of liquid crystal elastomer films can be effective lifters; devices that can generate thrust for...
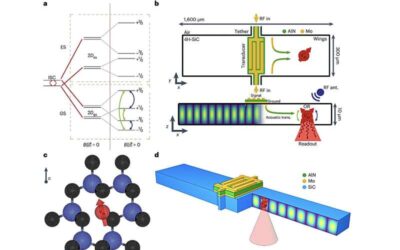
A strategy for the spin-acoustic control of silicon vacancies in a 4H silicon carbide-based bulk acoustic resonator
Bulk acoustic resonators—stacked material structures inside which acoustic waves resonate—can be used to amplify sounds or filter out undesired noise. These resonators have found wide use in today's RF telecommunication, like Front-End Modules (FEM) in iPhones. They...
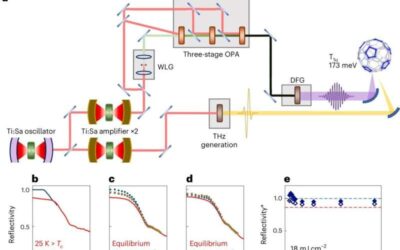
A strategy to enhance the light-driven superconductivity of K₃C₆₀
Superconductivity is the ability of some materials to conduct a direct electrical current (DC) with almost no resistance. This property is highly sought after and favorable for various technological applications, as it could boost the performance of different...
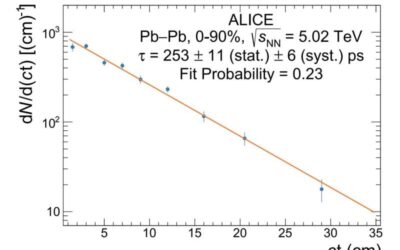
A new highly precise measurement of the hypertriton lifetime
A hypertriton is a tritium nucleus in which a neutron is replaced by a so-called Lambda hyperon. This type of hypernucleus was first discovered in the 1950s has since been the key focus of numerous studies.
Recent manipulations of excitons in moiré superlattices
Light can excite electron and hole pairs inside semiconducting materials. If the attraction between a negatively charged electron and a positively charged hole (the antiparticle of electron in solid state physics) is strong, they stay bound together, forming states...