The collective motion of animals in a group is a fascinating topic of research for many scientists. Understanding these collective behaviors can sometimes inspire the development of strategies for promoting positive social change, as well as technologies that emulate...
Physics
Recent searches for light fermionic dark matter by the PandaX-4T collaboration
Teams of astrophysicists worldwide are trying to observe different possible types of dark matter (DM), hypothetical matter in the universe that does not emit, absorb or reflect light and would thus be very difficult to detect. Fermionic DM, however, which would be...
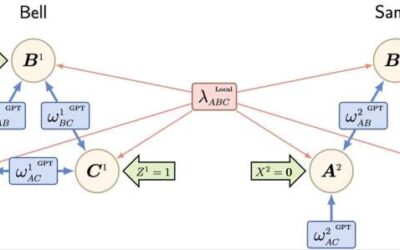
Study proves a generalization of Bell’s theorem: Quantum correlations are genuinely tripartite and nonlocal
Quantum theory predicts the existence of so-called tripartite-entangled states, in which three quantum particles are related in a way that has no counterpart in classical physics. Theoretical physicists would like to understand how well new theories, alternatives to...
Electrons with Planckian scattering in strange metals follow standard rules of orbital motion in a magnet
Strange metals, or non-Fermi liquids, are distinct states of matter that have been observed in different quantum materials, including cuprate superconductors. These states are characterized by unusual conductive properties, such as a resistivity that is linearly...
Exploring the decay processes of a quantum state weakly coupled to a finite-size reservoir
In quantum physics, Fermi's golden rule, also known as the golden rule of time-dependent perturbation theory, is a formula that can be used to calculate the rate at which an initial quantum state transitions into a final state, which is composed of a continuum of...
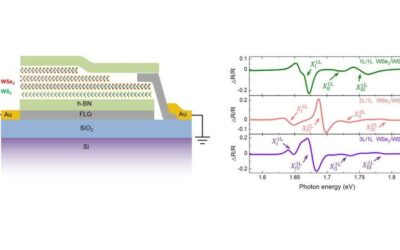
A design to tune moiré excitons in TMDC superlattices through varying layer degrees of freedom
Transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs) are an emerging and promising class of materials comprised of a transition metal atomic layer sandwiched between two layers of chalcogen atoms. These 2D materials have received considerable attention over the past few years, as...
The coherent simulation of a quantum phase transition in a programmable 2,000 qubit Ising chain
Quantum computers have the potential to outperform classical computers on several complex tasks, yet many challenges will need to be overcome before they reach their full potential. In the meantime, physicists and computer scientists have been trying to realistically...
A new method to enable efficient interactions between photons
Photons, particles that represent a quantum of light, have shown great potential for the development of new quantum technologies. More specifically, physicists have been exploring the possibility of creating photonic qubits (quantum units of information) that can be...
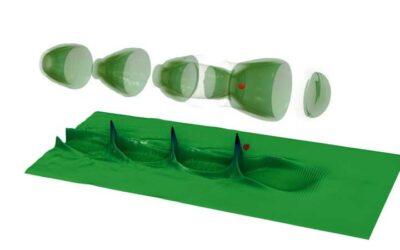
The direct observation of highly nonlinear plasma waves
Over the past few decades, physicists and engineers have been trying to create increasingly compact laser-plasma accelerators, a technology to study matter and particle interactions produced by interactions between ultrafast laser beams and plasma. These systems are a...
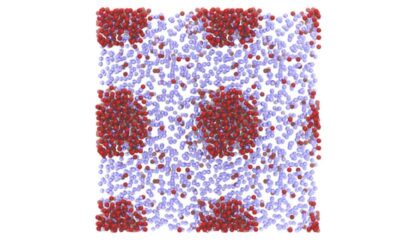
A new experimental study tackles the unsolved mystery of ‘nanobubbles’
Nanobubbles are extremely small (i.e., nanoscopic) gaseous cavities that some physicists observed in aqueous solutions, typically after specific substances were dissolved in them. While some studies reported the observation of these incredibly tiny bubbles, some...