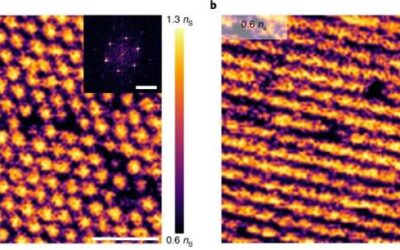
Moiré superlattices are systems in which two sheets of a material are placed on top of each other with a small angle misalignment, resulting in a characteristic pattern known as the Moiré pattern. In recent years, many physicists and material scientists have been...
Physics
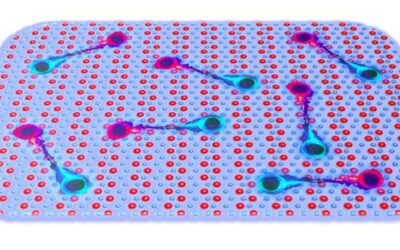
A device based on 3D transistor arrays for collecting intra and inter-cellular recordings
Animal cells can use elements or ions to generate electrical impulses. These impulses are then conveyed from one cell to another, traveling across cellular networks.
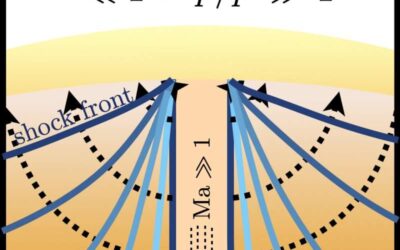
Dark matter travelling through stars could produce potentially detectable shock waves
Dark matter, a hypothetical material that does not absorb, emit or reflect light, is thought to account for over 80 percent of the matter in the universe. While many studies have indirectly hinted at its existence, so far, physicists have been unable to directly...
Study finds that black hole inner horizons can be charged or discharged
Black holes are intriguing and widely studied cosmic bodies with extremely high tidal forces, from which even light is unable to escape. While many studies predicted the existence of black holes, which have also recently been detected, many questions about these...
Study shows that monolayer tungsten ditelluride is an excitonic insulator
Tungsten ditelluride (WTe2) is a transition metal dichalcogenide with numerous advantageous properties and characteristics, which makes it an ideal material for a wide range of electronic applications. Past studies have established that 2D WTe2 crystals arranged...
Information processing constrains how E. coli bacteria navigate chemical gradients
Living organisms adapt their behavior and movements based on information they acquire from their surrounding environment. But oftentimes this information is imperfect, and the organism needs to act under uncertainty. So, does imperfect information limit an organism's...
Evidence of a quantum phase transition without symmetry breaking in cerium-cobalt-indium 5
Over the past few decades, many condensed matter physicists have conducted research focusing on quantum phase transitions that are not clearly associated with a broken symmetry. One reason that these transitions are interesting is that they might underpin the...
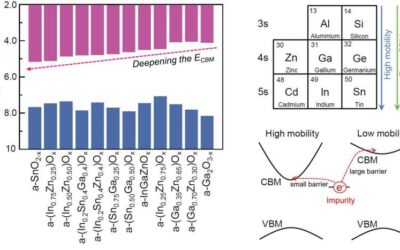
Exploring factors impacting the sensitivity of amorphous oxide semiconductors to externally induced impurities
In recent years, electronics engineers have been trying to broaden the pool of available semiconducting materials, to enable the development of a wider range of devices. One emerging class of semiconductors are amorphous oxide semiconductors (AOSs), which are...
Study re-examines the decay of 185Bi using state-of-the-art technologies
Researchers at University of Surrey, University of York, University of Edinburgh, and Argonne National Laboratory have recently revisited and solved some of the long-standing puzzles associated with the decay of 185Bi, the heaviest known proton-emitting nucleus....
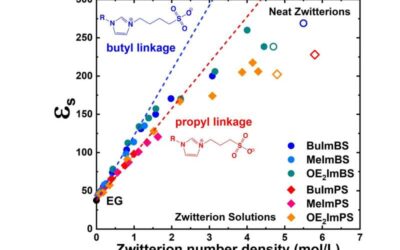
Study shows that zwitterions can raise the dielectric constant of soft materials
To create efficient energy storage solutions and actuators, engineers need materials with a high dielectric constant. The dielectric constant is essentially the ratio of a substance's permittivity (i.e., its ability to store electrical energy in an electric field) to...