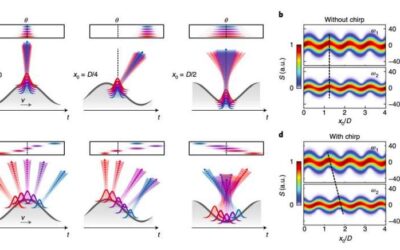
One of the topics investigated in recent physics studies is strong-field quantum electrodynamics (SF-QED). So far, this area has rarely been explored before, mainly because the experimental observation of SF-QED processes would require extremely high light intensities...
Physics
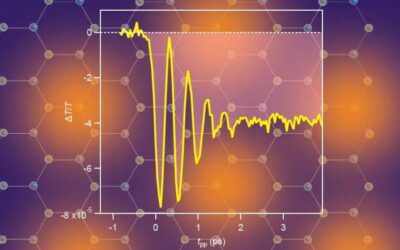
The demonstration of ultrafast switching to an insulating-like metastable state
In recent years, physicists and electronics engineers have been trying to devise strategies to control or produce quantum states of matter in different materials. Such strategies could ultimately prove valuable for the development of new technological devices.
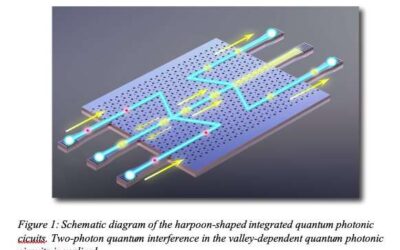
The realization of topologically protected valley-dependent quantum photonic chips
The field of topological photonics, specialized in the development of a class of materials known as photonic topological insulators, has advanced considerably over the past few decades. Photonic topological insulators have many promising qualities, including the...
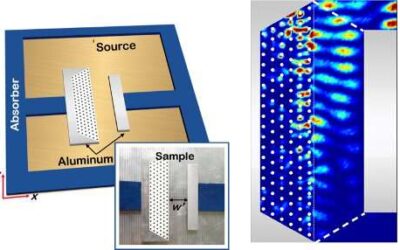
The first observation of the superscattering effect of metamaterials
Entering an invisible doorway to catch a train at King's Cross station in London is a renowned fictional scene from the Harry Potter series. In recent decades, physicists have been trying to produce a similar effect by focusing their research efforts on illusion...
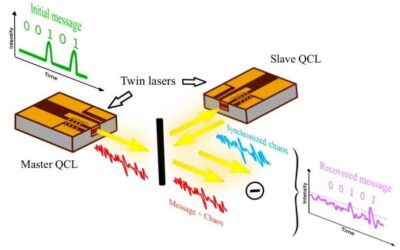
Researchers propose the use of quantum cascade lasers to achieve private free-space communications
Free-space optical communication, the communication between two devices at a distance using light to carry information, is a highly promising system for achieving high-speed communication. This system of communication is known to be immune to electromagnetic...
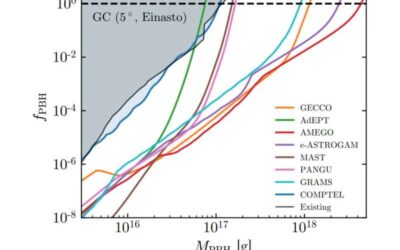
New possibilities for detecting Hawking radiation emitted by primordial black holes
While many physicists have predicted the existence of dark matter, a type of matter that does not absorb, reflect or emit light, so far no one has been able to observe it experimentally or determine its fundamental nature. Light primordial black holes (PBHs), black...
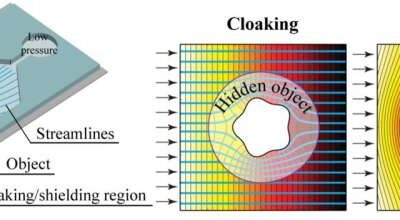
The demonstration of hydrodynamic cloaking and shielding at the microscale
Researchers at Technion—Israel Institute of Technology, Technische Universität Darmstadt, and IBM Research Europe have recently proposed a new strategy to simultaneously achieve microscale hydrodynamic cloaking and shielding. While the idea of cloaking or shielding...
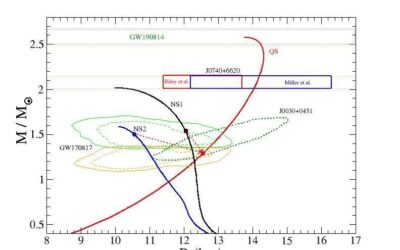
Could the source of the GW190814 event be a black hole-strange quark star system?
On the 14th of August 2019, the LIGO-Virgo collaboration detected a gravitational wave signal believed to be associated with the merging of a binary stellar system composed of a black hole with a mass of 23 times the mass of the sun (M⊙) and a compact object with a...
A framework to simulate the same physics using two different Hamiltonians
Researchers at Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University in Japan have recently been investigating situations in which two distinct Hamiltonians could be used to simulate the same physical phenomena. A Hamiltonian is a function or model used to...
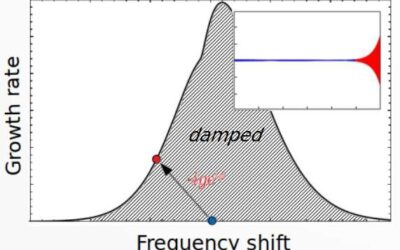
A procedure to directly measure the strength of Landau damping
Landau damping, a phenomenon originally predicted by Lev Landau in 1946, is essential to ensure the collective beam stability in particle accelerators. By precisely measuring the strength of Landau damping, physicists can predict the stability of beams in high-energy...