Superconductivity, which entails an electrical resistance of zero at very low temperatures, is a highly desirable and thus widely studied quantum phenomenon. Typically, this state is known to arise following the formation of bound electron pairs known as Cooper pairs,...
Physics
A new protocol to image wave functions in continuous space
In recent years, physicists have been trying to better understand the behavior of individual quantum particles as they move in space. Yet directly imaging these particles with high precision has so far proved challenging, due to the limitations of existing microscopy...
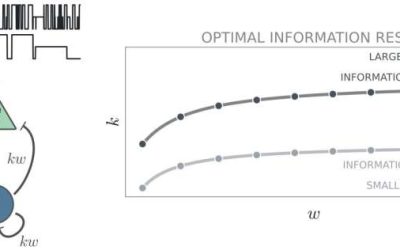
Optimal brain processing requires balance between excitatory and inhibitory neurons, study suggests
The brain's ability to process information is known to be supported by intricate connections between different neuron populations. A key objective of neuroscience research has been to delineate the processes via which these connections influence information processing.
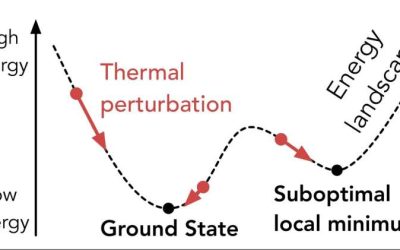
Quantum algorithm excels at finding local minima of many-body systems
Many physicists and engineers have recently been trying to demonstrate the potential of quantum computers for tackling some problems that are particularly demanding and are difficult to solve for classical computers. A task that has been found to be challenging for...
A new approach to reduce decoherence in superconducting qudit-based quantum processors
Quantum computers, which operate leveraging quantum mechanics effects, could soon outperform traditional computers in some advanced optimization and simulation tasks. Most quantum computing systems developed so far store and process information using qubits (quantum...
First dark matter search using WINERED spectrograph sets new lifetime constraints
Dark matter is an elusive type of matter that does not emit, absorb or reflect light and is thus impossible to detect using conventional techniques employed in particle physics. In recent years, groups of physicists worldwide have been trying to observe this matter...
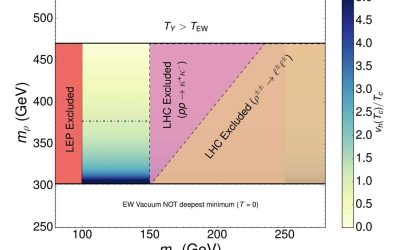
Hypercharge breaking scenarios could explain the baryon asymmetry of the universe
The Standard Model (SM), the main physics framework describing elementary particles and the forces driving them, outlines key patterns in physical interactions referred to as gauge symmetries. One of the symmetries it describes is the so-called U(1)Y hypercharge:...
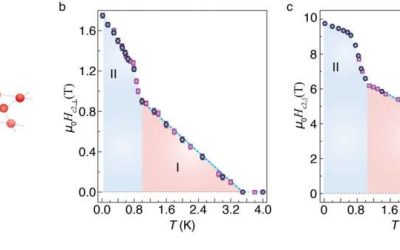
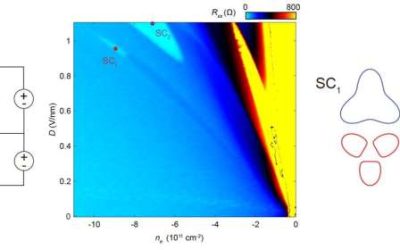
Two distinct superconducting states found in Bernal bilayer graphene challenge current models
Superconductivity is a widely sought after material property, which entails an electrical resistance of zero below a specific critical temperature. So far, it has been observed in various materials, including recently in so-called multilayer graphene allotropes (i.e.,...
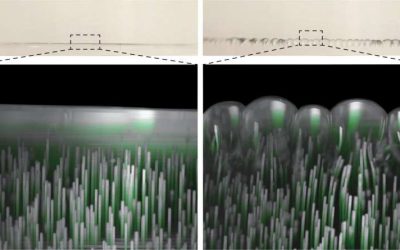
Study unveils new extrusion-induced instabilities in viscoelastic materials
Soft viscoelastic solids are flexible materials that can return to their original shape after being stretched. Due to the unique properties driving their deformation, these materials can sometimes behave and change shape in unexpected ways.
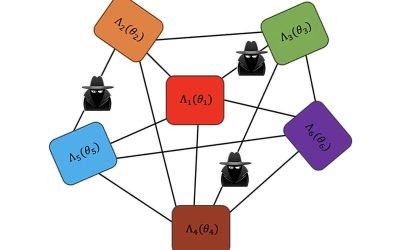
A newly proposed protocol to boost privacy in quantum sensor networks
Devices that leverage quantum mechanics effects, broadly referred to as quantum technologies, could help to tackle some real-world problems faster and more efficiently. In recent years, physicists and engineers have introduced various promising quantum technologies,...