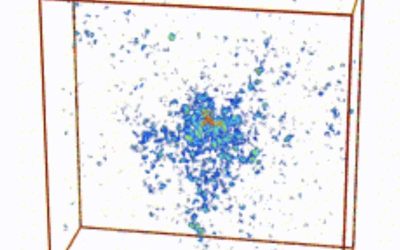
The Anderson transition is a phase transition that occurs in disordered systems, which entails a shift from a diffusive state (i.e., in which waves or particles are spread out) to a localized state, in which they are trapped in specific regions. This state was first...
Physics
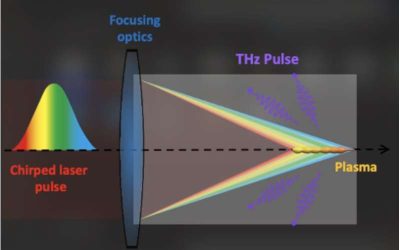
A promising technique to steer laser-produced THz radiation in air
Terahertz radiation (THz), electromagnetic radiation with frequencies ranging from 0.1 and 10 THz, is central to the functioning of various technologies, including imaging, sensing and spectroscopy tools. While THz radiation waves have been manipulated in different...
The ALPHA experiment moves towards the increasingly precise study of antihydrogen
Antimatter is a fascinating kind of matter made up of antiparticles, which have a mass equivalent to that of their normal matter counterparts, yet they exhibit an opposite charge and distinct quantum properties.
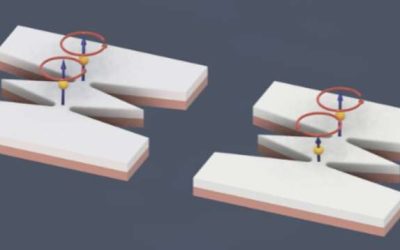
Researchers observe a phase transition in a 1D chain of atoms using a quantum simulator
Phase transitions, shifts between different states of matter, are widely explored physical phenomena. So far, these transitions have primarily been studied in three-dimensional (3D) and two-dimensional (2D) systems, yet theories suggest that they could also occur in...
Surface roughness disrupts glass transition in colloidal ellipsoids, offering a new material design parameter
The so-called glass transition is the process by which some liquid-like materials become solid-like, without forming a crystalline structure. In contrast to conventional solid materials, which exhibit an orderly atom arrangement, glass is characterized by a disordered...
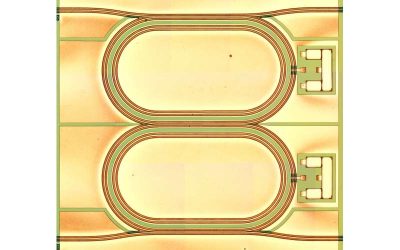
Study demonstrates phase-tunable spin-wave-mediated mutual synchronization of spin Hall nano-oscillators
Spin Hall nano-oscillators (SHNOs) are nanoscale spintronic devices that convert direct current into high-frequency microwave signals through spin wave auto-oscillations. This is a type of nonlinear magnetization oscillations that are self-sustained without the need...
Coupled semiconductor lasers generate novel optical patterns, enabling new spectroscopy techniques
The physical interaction between two or more systems, also known as coupling, can give rise to unique and unexpected effects. In the field of optics, coupled light sources (e.g., lasers) can influence each other, producing complex light patterns that cannot be emitted...
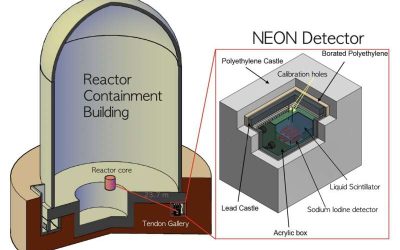
NEON experiment shares results from first direct search for light dark matter
Detecting dark matter, the elusive type of matter predicted to account for most of the universe's mass, has so far proved to be very challenging. While physicists have not yet been able to determine what exactly this matter consists of, various large-scale experiments...
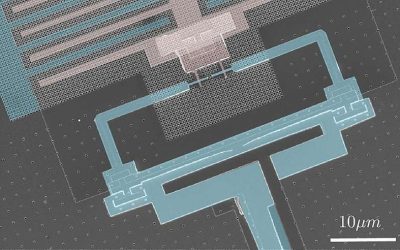
Using phononic bandgap materials to suppress decoherence in quantum computers
Quantum computers have the potential of outperforming classical computers on some optimization and computational tasks. Compared to classical systems, however, quantum systems are more prone to errors, as they are more sensitive to noise and prone to so-called...
Superionic compound with liquid-like dynamics shows promise as solid-state battery electrolyte
Superionic materials are a class of materials that simultaneously present properties that are characteristic of solids and liquids. Essentially, a set of ions in these materials exhibits liquid-like mobility, even if the materials' underlying atomic structure...