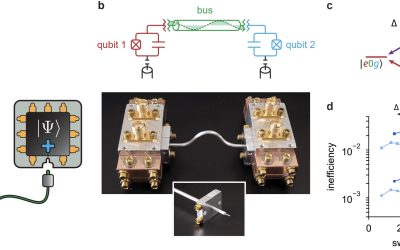
Quantum computers, devices that can perform computations relying on the principles of quantum mechanics, are expected to outperform classical computers on some types of optimization and processing tasks. While physicists and engineers have introduced various quantum...
Quantum Physics
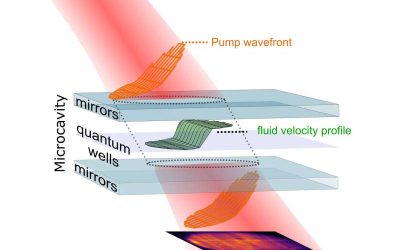
Simulating the Hawking effect and other quantum field theory predictions with polariton fluids
Quantum field theory (QFT) is a physics framework that describes how particles and forces behave based on principles rooted in quantum mechanics and Albert Einstein's special relativity theory. This framework predicts the emergence of various remarkable effects in...
Researchers uncover a topological excitonic insulator with a tunable momentum order
Topological materials are a class of materials that exhibit unique electronic properties at their boundary (surface in 3D materials; edge in 2D materials) that are robust against imperfections or disturbances and are markedly different from their bulk properties. In...
New scheme mitigates self-discharging in quantum batteries
Quantum batteries (QBs) are energy storage devices that could serve as an alternative to classical batteries, potentially charging faster and enabling the extraction of more energy. In contrast with existing batteries, these batteries leverage effects rooted in...
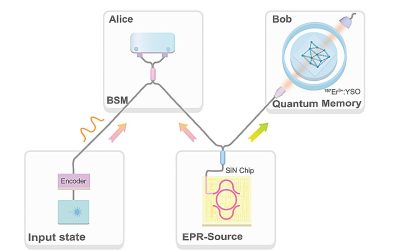
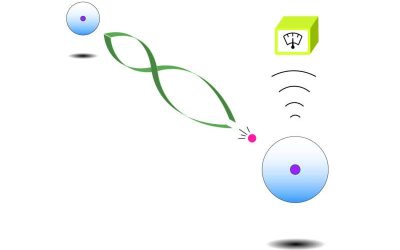
Quantum internet moves closer as researchers teleport light-based information
Quantum teleportation is a fascinating process that involves transferring a particle's quantum state to another distant location, without moving or detecting the particle itself. This process could be central to the realization of a so-called "quantum internet," a...
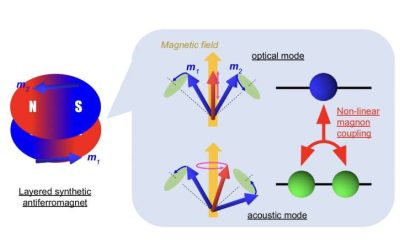
Rabi-like splitting arises from nonlinear interactions between magnons in synthetic antiferromagnet
Synthetic antiferromagnets are carefully engineered magnetic materials made up of alternating ferromagnetic layers with oppositely aligned magnetic moments, separated by a non-magnetic spacer. These materials can display interesting magnetization patterns,...
Quantum battery model achieves theoretical speed limit, demonstrates genuine advantage
Over the past few years, researchers have developed various quantum technologies, alternatives to classical devices that operate by leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics. These technologies have the potential to outperform their classical counterparts in...
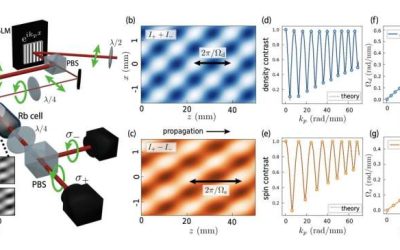
Scientists provide clear observation of spin and density modes in a two-component fluid of light
Recent physics studies have found that light can sometimes flow in unexpected ways, behaving like a so-called "superfluid." Superfluids, such as ultracold atomic gases or helium-4 below specific temperatures, are phases of matter characterized by flowing behavior with...
An approach to realize heralded photon storage in a Rydberg superatom
Quantum technologies, systems that operate leveraging quantum mechanical effects, have the potential to outperform classical technologies in some specific tasks. Over the past decades, some researchers have also been trying to realize quantum networks, systems...
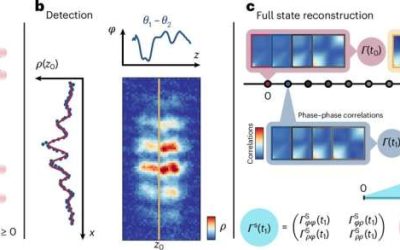
A new approach to probing Landauer’s principle in the quantum many-body regime
Landauer's principle is a thermodynamics concept also relevant in information theory, which states that erasing one bit of information from an information system results in the dissipation of at least a specific amount (i.e., kBTln2) of energy. This principle has...