Approximately 80% of the matter in the universe is predicted to be so-called "dark matter," which does not emit, reflect, or absorb light and thus cannot be directly detected using conventional experimental techniques.
Quantum Physics
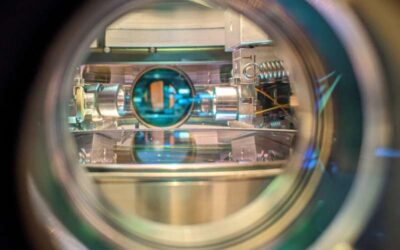
Generating graph states of atomic ensembles via photon-mediated entanglement
Graph states, a class of entangled quantum states that can be represented by graphs, have been the topic of numerous recent physics studies, due to their intriguing properties. These unique properties could make them particularly promising for quantum computing...
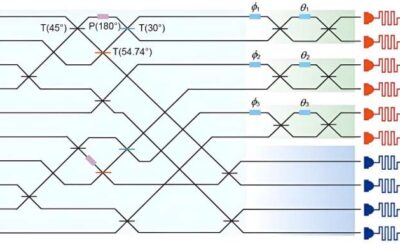
Demonstration of heralded three-photon entanglement on a photonic chip
Photonic quantum computers are computational tools that leverage quantum physics and utilize particles of light (i.e., photons) as units of information processing. These computers could eventually outperform conventional quantum computers in terms of speed, while also...
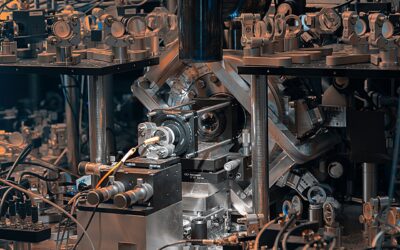
The experimental demonstration of a verifiable blind quantum computing protocol
Quantum computers, systems that process and store information leveraging quantum mechanical phenomena, could eventually outperform classical computers on numerous tasks. Among other things, these computers could allow researchers to tackle complex optimization...
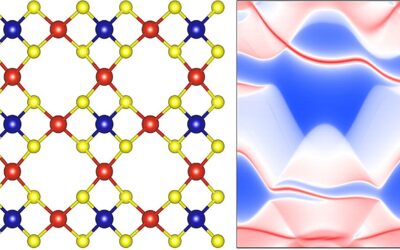
Study unveils a new family of quantum anomalous Hall insulators
In recent years, physicists and material scientists have identified various new materials marked by interesting properties and quantum effects. These materials could prove highly valuable both as platforms to study quantum effects and for the development of new...
A method to compute the Rényi entanglement entropy in auxiliary-field quantum Monte Carlo simulations
Entanglement is a widely studied quantum physics phenomenon, in which two particles become linked in such a way that the state of one affects the state of another, irrespective of the distance between them. When studying systems comprised of several strongly...
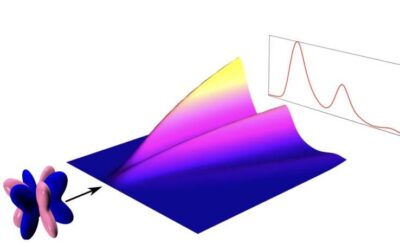
Study outlines spectroscopic signatures of fractionalization in octupolar quantum spin ice
Quantum spin liquids are fascinating quantum systems that have recently attracted significant research attention. These systems are characterized by a strong competition between interactions, which prevents the establishment of a long-range magnetic order, such as...
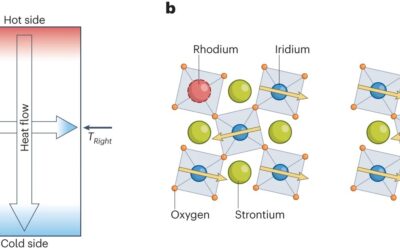
Evidence of phonon chirality from impurity scattering in the antiferromagnetic insulator strontium iridium oxide
The thermal hall effect (THE) is a physical phenomenon characterized by tiny transverse temperature differences occurring in a material when a thermal current passes through it and a perpendicular magnetic field is applied to it. This effect has been observed in a...
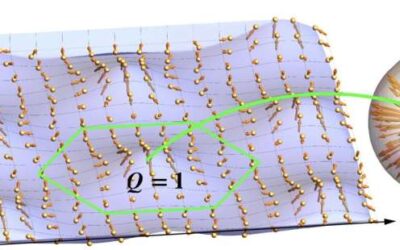
Researchers offer theoretical description of topological water wave structures
Topological wave structures are wave patterns that exhibit specific topological properties, or in other words, properties that remain unvaried under smooth deformations of a physical system. These structures, such as vortices and skyrmions, have attracted significant...
Diamond quantum memory with Germanium vacancy exceeds coherence time of 20 ms
The color centers of diamond are the focus of an increasing number of research studies, due to their potential for developing quantum technologies. Some works have particularly explored the use of negatively-charged group-IV diamond defects, which exhibit an efficient...