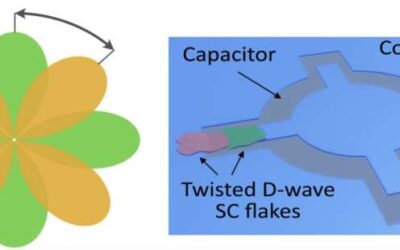
Quantum technology could outperform conventional computers on some advanced optimization and computational tasks. In recent years, physicists have been working to identify new strategies to create quantum systems and promising qubits (i.e., basic units of information...
Quantum Physics
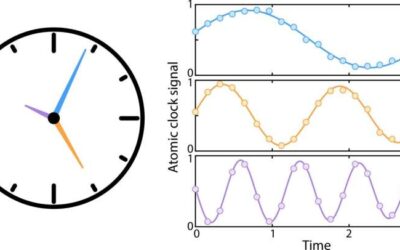
A multi-ensemble atomic clock enhanced using quantum computing tools
Atomic clocks are a class of clocks that leverage resonance frequencies of atoms to keep time with high precision. While these clocks have become increasingly advanced and accurate over the years, existing versions might not best utilize the resources they rely on to...
Researchers demonstrate multi-photon state transfer between remote superconducting nodes
Over the past few decades, quantum physicists and engineers have been trying to develop new, reliable quantum communication systems. These systems could ultimately serve as a testbed to evaluate and advance communication protocols.
Evidence that atomically thin hafnium telluride is an excitonic insulator
The condensation of excitons with non-zero momentum can give rise to so-called charge density waves (CDW). This phenomenon can prompt the transition of materials into a fascinating new quantum phase, known as an excitonic insulator.
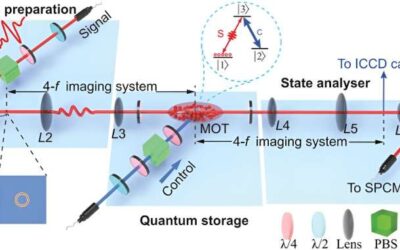
A new approach to realize highly efficient, high-dimensional quantum memories
Many physicists and engineers have been trying to develop highly efficient quantum technologies that can perform similar functions to conventional electronics leveraging quantum mechanical effects. This includes high-dimensional quantum memories, storage devices with...
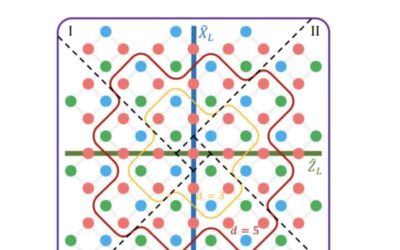
A logical magic state with fidelity beyond distillation threshold realized on superconducting quantum processor
Quantum computers have the potential to outperform conventional computers on some tasks, including complex optimization problems. However, quantum computers are also vulnerable to noise, which can lead to computational errors.
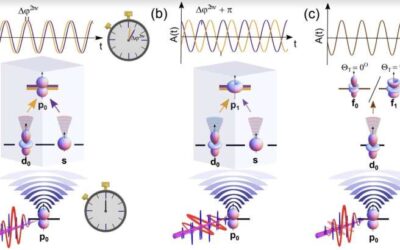
A method to resolve quantum interference between photoionization pathways with attosecond resolution
The field of attosecond physics was established with the mission of exploring light–matter interactions at unprecedented time resolutions. Recent advancements in this field have allowed physicists to shed new light on the quantum dynamics of charge carriers in atoms...
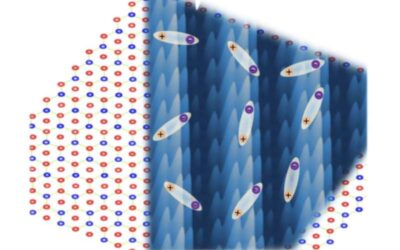
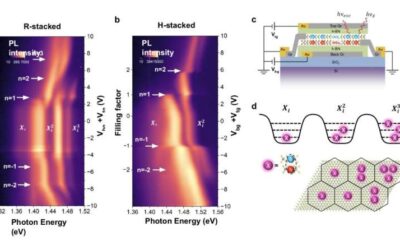
The formation of an excitonic Mott insulator state in a moiré superlattice
When a negatively charged electron and a positively charged hole in a pair remain bound together following excitation by light, they produce states known as excitons. These states can influence the optical properties of materials, in turn enabling their use for...
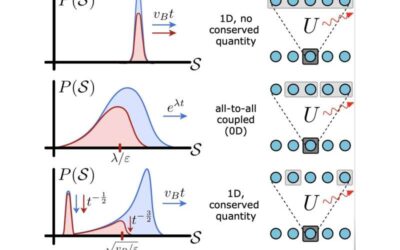
A universal framework describing the scrambling of quantum information in open systems
In recent years, physicists have been trying to better understand how quantum information spreads in systems of interacting particles—a phenomenon often referred to as "scrambling." Scrambling in closed systems, physical systems that can only exchange energy with...
Muon g-2 experiment measures the positive muon anomalous magnetic moment to 0.20 ppm
The Muon g-2 Collaboration is a large group of researchers at different institutes worldwide collaborating on the Muon g-2 experiment. This is a research effort aimed at exploring the interactions of muons, short-lived particles that are essentially heavy electrons,...