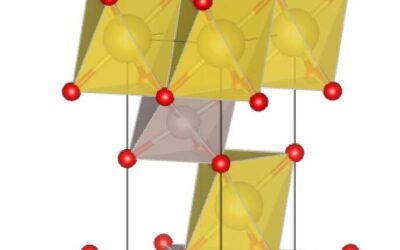
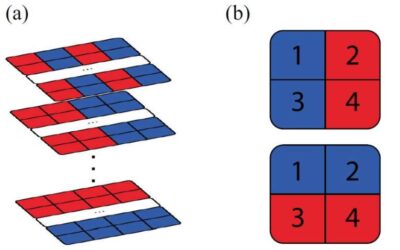
Magnetic materials with a triangular lattice have been the focus of numerous research studies, as theoretical predictions suggest that they could exhibit spin liquid states. These are quantum phases of matter that present interesting characteristics, such as quantum...
Quantum Physics
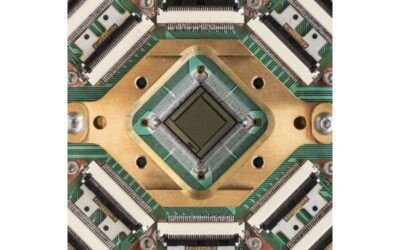
Team demonstrates quantum advantage on optimization problems with a 5,000-qubit programmable spin glass
Over the past decades, researchers and companies worldwide have been trying to develop increasingly advanced quantum computers. The key objective of their efforts is to create systems that will outperform classical computers on specific tasks, which is also known as...
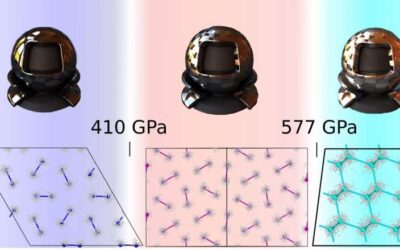
The comprehensive characterization of hydrogen at ultra-high pressures
Physicists and material scientists have been trying to metallize hydrogen for many decades, but they have not yet succeeded. In 1968, British physicist Neil Ashcroft predicted that atomic metallic hydrogen would be a high-temperature semiconductor.
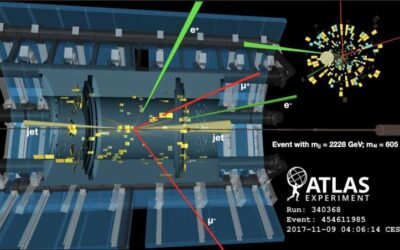
The ATLAS collaboration observes the electroweak production of two jets and a Z-boson pair
The ATLAS collaboration, the large research consortium involved in analyzing data collected by the ATLAS particle collider at CERN, recently observed the electroweak production of two Z bosons and two jets. This crucial observation, presented in Nature Physics,...
A universal protocol that inverts the evolution of a qubit with a high probability of success
Researchers at the Institute for Quantum Optics and Quantum Information (IQOQI) in Vienna recently devised a universal mechanism to invert the evolution of a qubit with a high probability of success. This protocol, outlined in Physical Review Letters, can...
A robust quantum memory that stores information in a trapped-ion quantum network
Researchers at University of Oxford have recently created a quantum memory within a trapped-ion quantum network node. Their unique memory design, introduced in a paper in Physical Review Letters, has been found to be extremely robust, meaning that it could store...
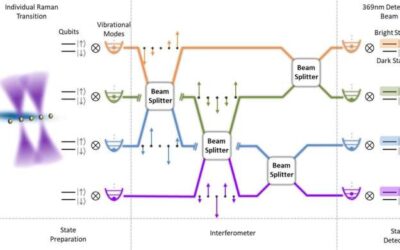
A scalable and programmable quantum phononic processor based on trapped ions
Quantum computing systems have the potential to outperform classical computers on some tasks, helping to solve complex real-world problems in shorter times. Research teams worldwide have thus been trying to realize this quantum advantage over traditional computers, by...
The experimental observation of quantum avalanches in a many-body localized system
Strongly correlated systems are systems made of particles that strongly interact with one another, to such an extent that their individual behavior depends on the behavior of all other particles in the system. In states that are far from equilibrium, these systems can...
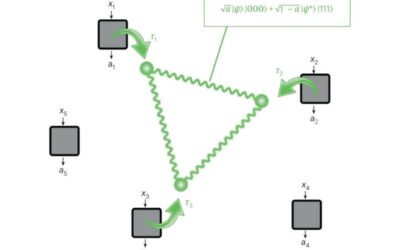
A framework to self-test all entangled states using quantum networks
Self-testing is a promising method to infer the physics underlying specific quantum experiments using only collected measurements. While this method can be used to examine bipartite pure entangled states, so far it could only be applied to limited kinds of quantum...
The experimental realization of quantum overlapping tomography
Quantum tomography is a process that involves the reconstruction and characterization of a quantum state using a series of collected measurements. Over the past few years, many physicists have been trying to use this process to learn more about quantum states, as this...