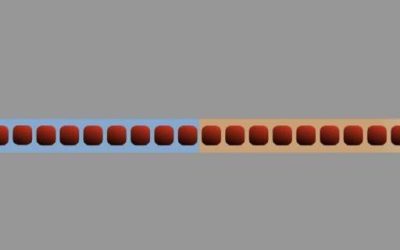
Embezzlement of entanglement is an exotic phenomenon in quantum information science, describing the possibility of extracting entanglement from a resource system without changing its quantum state. In this context, the resource systems play the role of a catalyst,...
Quantum Physics
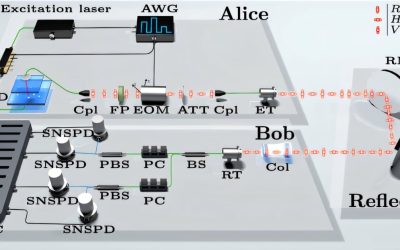
True single-photon source boosts secure key rates in quantum key distribution systems
Quantum key distribution (QKD), a cryptographic technique rooted in quantum physics principles, has shown significant potential for enhancing the security of communications. This technique enables the transmission of encryption keys using quantum states of photons or...
Atom tweezer arrays reveal how phase transitions unfold in mesoscopic systems
As the number of particles in a physical system increases, its properties can change and different phase transitions (i.e., shifts into different phases of matter) can take place. Microscopic systems (i.e., containing only a few particles) and macroscopic ones (i.e.,...
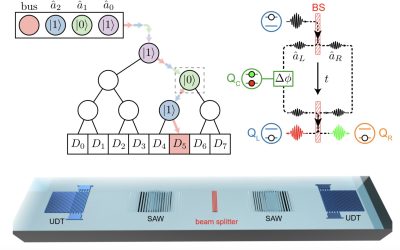
A quantum random access memory based on transmon-controlled phonon routers
Recent technological advances have opened new exciting possibilities for the development of cutting-edge quantum devices, including quantum random access memory (QRAM) systems. These are memory architectures specifically meant to be integrated inside quantum...
Nonreciprocal light speed control achieved using cavity magnonics device
The reliable manipulation of the speed at which light travels through objects could have valuable implications for the development of various advanced technologies, including high-speed communication systems and quantum information processing devices. Conventional...
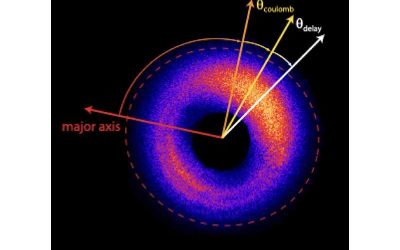
Phase-resolved attoclock precisely measures electron tunneling time
When placed under a powerful laser field (i.e., under strong-field ionization), electrons can temporarily cross the so-called quantum tunneling barrier, an energy barrier that they would typically be unable to overcome. This quantum mechanics phenomenon, known as...
General framework bridges quantum thermodynamics and non-Markovianity
The extraction of work (i.e., usable energy) from quantum processes is a key focus of quantum thermodynamics research, which explores the application of thermodynamics laws to quantum systems. Meanwhile, other quantum physics research has been investigating the...
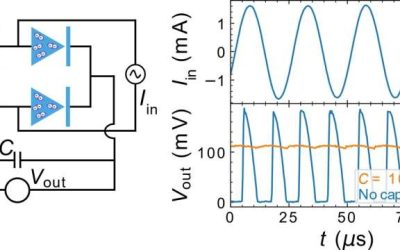
Superconducting diode bridge efficiently converts AC to DC for quantum circuits
Superconductivity is an advantageous property observed in some materials, which entails an electrical resistance of zero at extremely low temperatures. Superconductors, materials that exhibit this property, have proved to be highly promising for the development of...
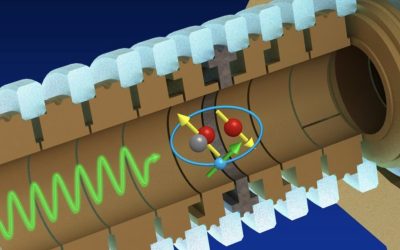
A new method to control the rovibrational ground state of a single molecular hydrogen ion
The precise measurement of states in atomic and molecular systems can help to validate fundamental physics theories and their predictions. Among the various platforms that can help to validate theoretical predictions are so-called diatomic molecular hydrogen ions...
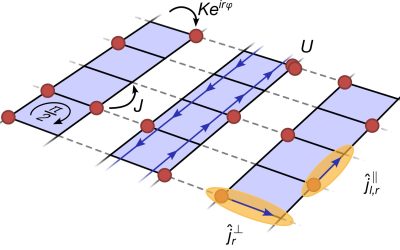
Quantum simulator realizes strongly interacting Mott-Meissner phases in bosonic flux ladders
When exposed to periodic driving, which is the time-dependent manipulation of a system's parameters, quantum systems can exhibit interesting new phases of matter that are not present in time-independent (i.e., static) conditions. Among other things, periodic driving...