When two-dimensional electron systems are subjected to magnetic fields at low temperatures, they can exhibit interesting states of matter, such as fractional quantum Hall liquids. These are exotic states of matter characterized by fractionalized excitations and the...
Quantum Physics
Two distinct exciton states observed in 2H stacked bilayer molybdenum diselenide
Two-dimensional (2D) materials have proved to be a promising platform for studying exotic quasiparticles, such as excitons. Excitons are bound states that emerge when an electron in a material absorbs energy and rises to a higher energy level, leaving a hole (i.e.,...
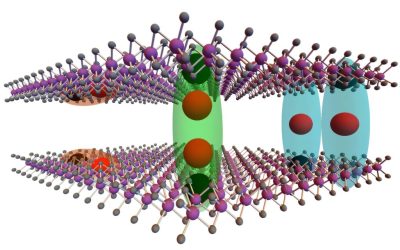
Two distinct exciton states observed in 2H stacked bilayer molybdenum diselenide
Two-dimensional (2D) materials have proved to be a promising platform for studying exotic quasiparticles, such as excitons. Excitons are bound states that emerge when an electron in a material absorbs energy and rises to a higher energy level, leaving a hole (i.e.,...
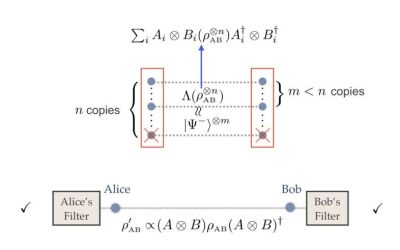
A scalable approach to distill quantum features from higher-dimensional entanglement
The operation of quantum technologies relies on the reliable realization and control of quantum states, particularly entanglement. In the context of quantum physics, entanglement entails a connection between particles, whereby measuring one determines the result of...
New microwave-to-optical transducer uses rare-earth ions for efficient quantum signal conversion
Quantum technologies, which leverage quantum mechanical effects to process information, could outperform their classical counterparts in some complex and advanced tasks. The development and real-world deployment of these technologies partly relies on the ability to...
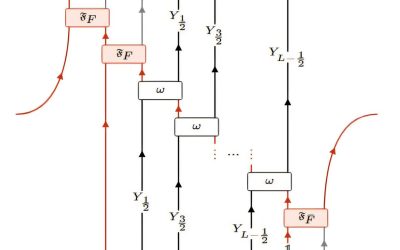
Study shows that duality operators can be realized as unitary linear-depth quantum circuits
In the context of quantum physics, the term "duality" refers to transformations that link apparently distinct physical theories, often unveiling hidden symmetries. Some recent studies have been aimed at understanding and implementing duality transformations, as this...
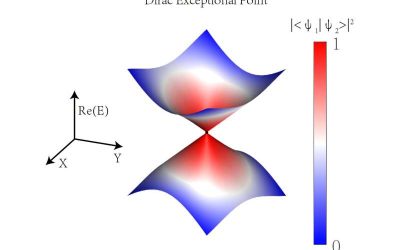
The first experimental observation of Dirac exceptional points
Exceptional points (EPs) are unique types of energy-level degeneracies that occur in non-Hermitian systems. Since their existence was first proposed more than a century ago, physicists have only been able to experimentally observe two types of EPs, both of which were...
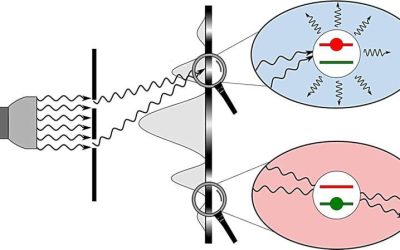
New quantum optics theory proposes that classical interference arises from bright and dark states of light
Classical physics theories suggest that when two or more electromagnetic waves interfere destructively (i.e., with their electric fields canceling each other out), they cannot interact with matter. In contrast, quantum mechanics theory suggests that light particles...
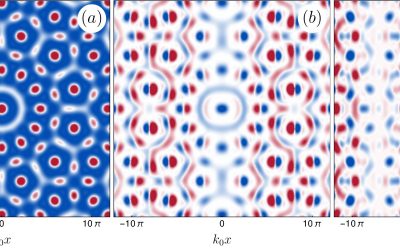
New physics theory to study low-energy excitations in quantum quasicrystals
Quasicrystals, exotic states of matter characterized by an ordered structure with non-repeating spatial patterns, have been the focus of numerous recent physics studies due to their unique organization and resulting symmetries. Among the quasicrystals that have...
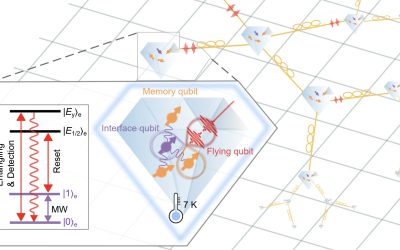
Researchers attain coherent control of a hybrid quantum network node
Quantum technologies, which operate leveraging quantum mechanical phenomena, have the potential to outperform their classical counterparts in some optimization and computational tasks. These technologies include so-called quantum networks, systems designed to transmit...