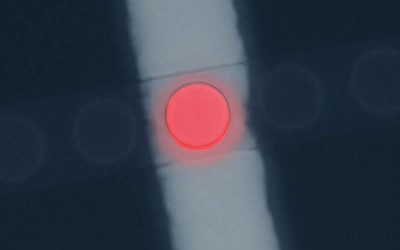
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are widely used electroluminescent devices that emit light in response to an applied electric voltage. These devices are central components of various electronic and optoelectronic technologies, including displays, sensors and...
Quantum Physics
Quantum entanglement wins: Researchers report quantum advantage in a simple cooperation game
Quantum systems hold the promise of tackling some complex problems faster and more efficiently than classical computers. Despite their potential, so far only a limited number of studies have conclusively demonstrated that quantum computers can outperform classical...
A new protocol to image wave functions in continuous space
In recent years, physicists have been trying to better understand the behavior of individual quantum particles as they move in space. Yet directly imaging these particles with high precision has so far proved challenging, due to the limitations of existing microscopy...
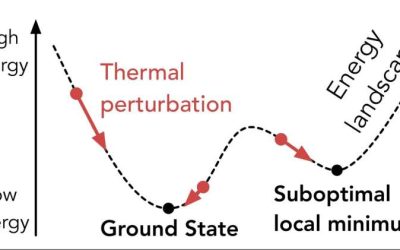
Quantum algorithm excels at finding local minima of many-body systems
Many physicists and engineers have recently been trying to demonstrate the potential of quantum computers for tackling some problems that are particularly demanding and are difficult to solve for classical computers. A task that has been found to be challenging for...
A new approach to reduce decoherence in superconducting qudit-based quantum processors
Quantum computers, which operate leveraging quantum mechanics effects, could soon outperform traditional computers in some advanced optimization and simulation tasks. Most quantum computing systems developed so far store and process information using qubits (quantum...
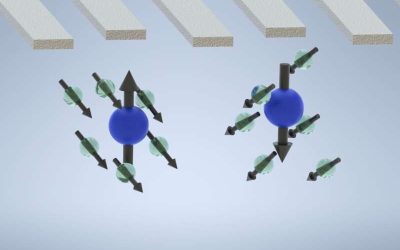
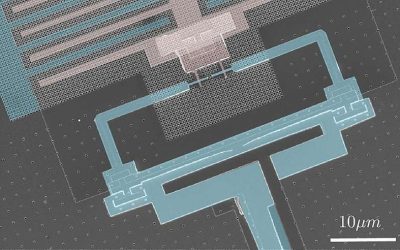
Newly realized nuclear-spin dark state promises reduced quantum decoherence
Quantum computers, which operate leveraging quantum mechanics phenomena, could eventually tackle some optimization and computational problems faster and more efficiently than their classical counterparts. Instead of bits, the fundamental units of information in...
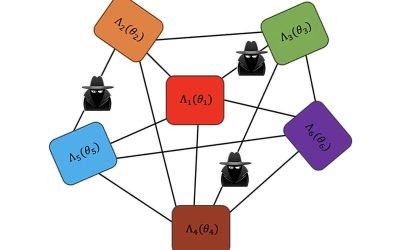
A newly proposed protocol to boost privacy in quantum sensor networks
Devices that leverage quantum mechanics effects, broadly referred to as quantum technologies, could help to tackle some real-world problems faster and more efficiently. In recent years, physicists and engineers have introduced various promising quantum technologies,...
Researchers observe a phase transition in a 1D chain of atoms using a quantum simulator
Phase transitions, shifts between different states of matter, are widely explored physical phenomena. So far, these transitions have primarily been studied in three-dimensional (3D) and two-dimensional (2D) systems, yet theories suggest that they could also occur in...
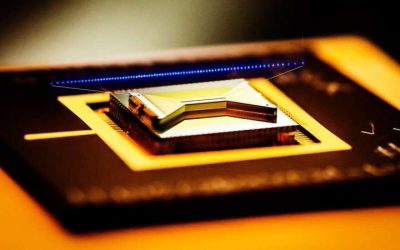
Using phononic bandgap materials to suppress decoherence in quantum computers
Quantum computers have the potential of outperforming classical computers on some optimization and computational tasks. Compared to classical systems, however, quantum systems are more prone to errors, as they are more sensitive to noise and prone to so-called...
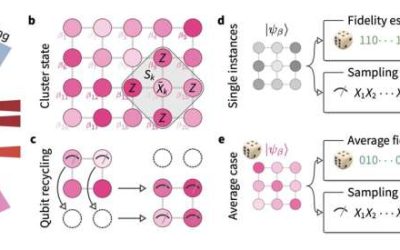
Trapped-ion processor demonstrates verifiable quantum random sampling
One of the key goals within the field of quantum computing is to achieve what is known as a quantum advantage. This term essentially describes the point after which a quantum computer can outperform a classical computer on a specific task or solve a problem that is...