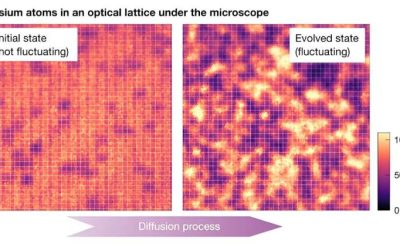
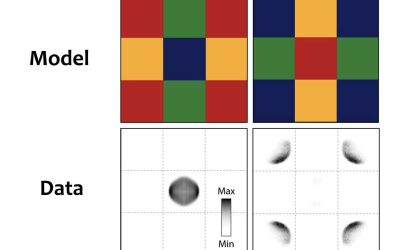
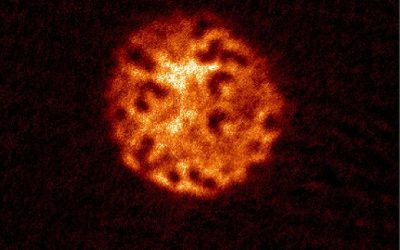
Researchers at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität, Max-Planck-Institut für Quantenoptik, Munich Center for Quantum Science and Technology (MCQST) and the University of Massachusetts recently carried out a study investigating the equilibrium fluctuations in large quantum...
Quantum Physics
Study predicts a new quantum anomalous crystal in fractionally filled moiré superlattices
Moiré superlattices, structures that arise when two layers of two-dimensional (2D) materials are overlaid with a small twist angle, have been the focus of numerous physics studies. This is because they have recently been found to host novel fascinating unobserved...
Study uncovers condensed-matter dark states in a quantum system with two pairs of sublattices
Dark states are quantum states in which a system does not interact with external fields, such as light (i.e., photons) or electromagnetic fields. These states, which generally occur due to interferences between the pathways through which a system interacts with an...
Physicists successfully observe Kibble–Zurek scaling in an atomic Fermi superfluid
The Kibble–Zurek (KZ) mechanism is a theoretical framework introduced by physicists Tom Kibble and Wojciech Zurek. This framework essentially describes the formation of topological defects while systems undergo non-equilibrium phase transitions.
Study unveils limits on the extent to which quantum errors can be ‘undone’ in large systems
Quantum computers have the potential of outperforming conventional computers on some practically relevant information processing problems, possibly even in machine learning and optimization. Yet their large-scale deployment is not yet feasible, largely due to their...
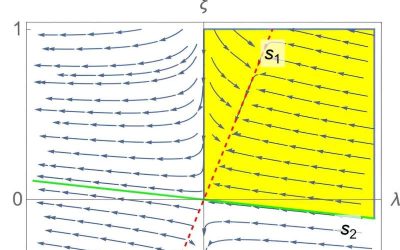
A new technique to calculate the physical running of couplings in quadratic gravity
Researchers at the International School for Advanced Studies in Trieste, University of Massachusetts, and Instituto de Física Teórica at Universidade Estadual Paulista in Brazil recently introduced an alternative approach to derive the correct physical beta functions...
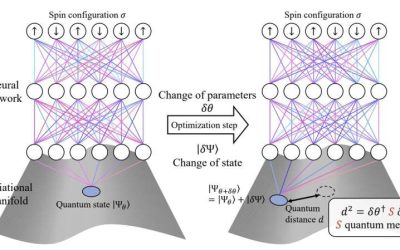
Optimization algorithm successfully computes the ground state of interacting quantum matter
Over the past decades, computer scientists have developed various computing tools that could help to solve challenges in quantum physics. These include large-scale deep neural networks that can be trained to predict the ground states of quantum systems. This method is...
An optical lattice clock based on strontium atoms achieves unprecedented accuracy
Researchers at the Ye Lab at JILA (the National Institute of Standards and Technology and the University of Colorado Boulder) and University of Delaware recently created a highly precise optical lattice clock based on trapped strontium atoms. Their...
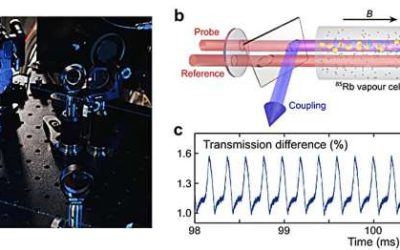
The experimental observation of a dissipative time crystal in a Rydberg gas
A dissipative time crystal is a phase of matter characterized by periodic oscillations over time, while a system is dissipating energy. In contrast with conventional time crystals, which can also occur in closed systems with no energy loss, dissipative time crystals...
Visualizing the boundary modes of the charge density wave in a topological material
Charge density waves are quantum phenomena occurring in some materials, which involve a static modulation of conduction electrons and the periodic distortion of the lattice. These waves have been observed in numerous condensed matter materials, including...